An appraisal of the current status of inhibition of glucose transporters as an emerging antineoplastic approach: Promising potential of new pan-GLUT inhibitors
- PMID: 36386187
- PMCID: PMC9663470
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1035510
An appraisal of the current status of inhibition of glucose transporters as an emerging antineoplastic approach: Promising potential of new pan-GLUT inhibitors
Abstract
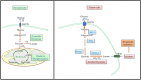
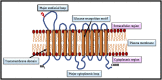
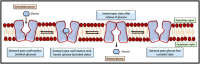
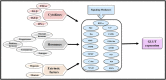
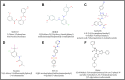
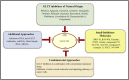
Neoplastic cells displayed altered metabolism with accelerated glycolysis. Therefore, these cells need a mammoth supply of glucose for which they display an upregulated expression of various glucose transporters (GLUT). Thus, novel antineoplastic strategies focus on inhibiting GLUT to intersect the glycolytic lifeline of cancer cells. This review focuses on the current status of various GLUT inhibition scenarios. The GLUT inhibitors belong to both natural and synthetic small inhibitory molecules category. As neoplastic cells express multiple GLUT isoforms, it is necessary to use pan-GLUT inhibitors. Nevertheless, it is also necessary that such pan-GLUT inhibitors exert their action at a low concentration so that normal healthy cells are left unharmed and minimal injury is caused to the other vital organs and systems of the body. Moreover, approaches are also emerging from combining GLUT inhibitors with other chemotherapeutic agents to potentiate the antineoplastic action. A new pan-GLUT inhibitor named glutor, a piperazine-one derivative, has shown a potent antineoplastic action owing to its inhibitory action exerted at nanomolar concentrations. The review discusses the merits and limitations of the existing GLUT inhibitory approach with possible future outcomes.
Keywords: GLUT; glutor; neoplastic cells; pan-GLUT inhibitors; tumor metabolism.
Copyright © 2022 Temre, Kumar and Singh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glutor, a Glucose Transporter Inhibitor, Exerts Antineoplastic Action on Tumor Cells of Thymic Origin: Implication of Modulated Metabolism, Survival, Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Membrane Potential, pH Homeostasis, and Chemosensitivity.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 30;12:925666. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.925666. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847943 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of glutor-GLUT interaction and prediction of glutor's drug-likeness: implications for its utility as an antineoplastic agent.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023 Dec;41(20):11262-11273. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2022.2161010. Epub 2022 Dec 26. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023. PMID: 36571488
-
Power of two: combination of therapeutic approaches involving glucose transporter (GLUT) inhibitors to combat cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020 Dec;1874(2):188457. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188457. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33096154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A small-molecule pan-class I glucose transporter inhibitor reduces cancer cell proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in vivo by targeting glucose-based metabolism.Cancer Metab. 2021 Mar 26;9(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s40170-021-00248-7. Cancer Metab. 2021. PMID: 33771231 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Glucose Transporter (GLUT) Inhibitors.European J Org Chem. 2020 May 3;2020(16):2321-2329. doi: 10.1002/ejoc.201901353. Epub 2019 Nov 28. European J Org Chem. 2020. PMID: 32421048 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An alternative way to break the matrix barrier: an experimental study of a LIFU-mediated, visualizable targeted nanoparticle synergistic amplification for the treatment of malignant fibroblasts.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Nov 5;12:1486369. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1486369. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39564102 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Reduction of Glut1 Normalizes Retinal Dysfunction, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress in the Retina of Spontaneous Type 2 Diabetic Mice.Am J Pathol. 2023 Jul;193(7):927-938. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2023.04.003. Epub 2023 Apr 14. Am J Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37062410 Free PMC article.
-
The Involvement of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Alteration in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Clinical Implication.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Apr 26;16:1837-1852. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S398291. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37131409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The combined treatment with ketogenic diet and metformin slows tumor growth in two mouse models of triple negative breast cancer.Transl Med Commun. 2024;9(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s41231-024-00178-8. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Transl Med Commun. 2024. PMID: 39574543 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic targeting of cancer associated fibroblasts overcomes T-cell exclusion and chemoresistance in soft-tissue sarcomas.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 20;15(1):2498. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46504-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38509063 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

