Development and Validation of a Nomogram for Prediction of the Risk of MAFLD in an Overweight and Obese Population
- PMID: 36381091
- PMCID: PMC9634768
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2021.00317
Development and Validation of a Nomogram for Prediction of the Risk of MAFLD in an Overweight and Obese Population
Abstract
Background and aims: Metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is a serious condition, and a simple method is needed for practitioners to identify patients with the disease and have a high risk of disease progression.
Methods: We developed and validated a nomogram for fatty liver disease and reclassified the risk factors for MAFLD. The development cohort had 335 patients who received bioelectrical impedance analysis and liver ultrasound attenuation measurements at Shenzhen People's Hospital between September 2020 and June 2021. The validation cohort had 200 patients from other hospitals who received the same evaluation. A random forest procedure and binary logistic analysis were used to screen for risk factors, establish a fatty liver disease predictive model, and forecast the risk of MAFLD. The performance of the nomogram was evaluated by measurement of discrimination, calibration, and clinical usefulness.
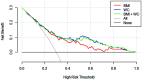
Results: The nomogram provided good predictions in a model that included body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference. The areas under the curve of the nomogram were 0.793 in the development cohort and 0.774 in the validation cohort. The nomogram performed well for calibration, category-free net reclassification improvement, and integrated discrimination improvement. Decision curve analysis indicated the nomogram performed better than BMI for predicting net outcome.
Conclusions: The nomogram was an effective screening tool for fatty liver disease, and for those overweight individuals, may help physicians make appropriate decisions regarding treatment of MAFLD.
Keywords: Body composition; Liver ultrasound attenuation, LiSA; MAFLD; Nomogram; Obesity.
© 2022 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a nomogram model for predicting the risk of MAFLD in the young population.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 23;14(1):9376. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60100-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38654043 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in the Chinese physical examination population.Lipids Health Dis. 2023 Jun 29;22(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01850-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2023. PMID: 37386566 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a new nomogram to screen for MAFLD.Lipids Health Dis. 2022 Dec 8;21(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01748-1. Lipids Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 36482400 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a predictive nomogram for the risk of MAFLD in postmenopausal women.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 6;15:1334924. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1334924. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39165508 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment and Analysis of Risk Prediction Model for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Physical Examination Population].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 May;54(3):591-595. doi: 10.12182/20230560109. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37248589 Free PMC article. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Institutional Nomogram for Estimating Risk of Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD).Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Oct 10;17:3735-3752. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S469677. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39403553 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nomogram model for predicting the risk of MAFLD in the young population.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 23;14(1):9376. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60100-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38654043 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in the Chinese physical examination population.Lipids Health Dis. 2023 Jun 29;22(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01850-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2023. PMID: 37386566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384(9945):766–781. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
