X-linked variations in SHROOM4 are implicated in congenital anomalies of the urinary tract and the anorectal, cardiovascular and central nervous systems
- PMID: 36379543
- PMCID: PMC10262053
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg-2022-108738
X-linked variations in SHROOM4 are implicated in congenital anomalies of the urinary tract and the anorectal, cardiovascular and central nervous systems
Abstract
Background: SHROOM4 is thought to play an important role in cytoskeletal modification and development of the early nervous system. Previously, single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) or copy number variations (CNVs) in SHROOM4 have been associated with the neurodevelopmental disorder Stocco dos Santos syndrome, but not with congenital anomalies of the urinary tract and the visceral or the cardiovascular system.
Methods: Here, exome sequencing and CNV analyses besides expression studies in zebrafish and mouse and knockdown (KD) experiments using a splice blocking morpholino in zebrafish were performed to study the role of SHROOM4 during embryonic development.
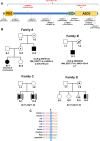
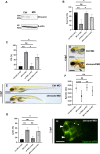
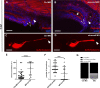
Results: In this study, we identified putative disease-causing SNVs and CNVs in SHROOM4 in six individuals from four families with congenital anomalies of the urinary tract and the anorectal, cardiovascular and central nervous systems (CNS). Embryonic mouse and zebrafish expression studies showed Shroom4 expression in the upper and lower urinary tract, the developing cloaca, the heart and the cerebral CNS. KD studies in zebrafish larvae revealed pronephric cysts, anomalies of the cloaca and the heart, decreased eye-to-head ratio and higher mortality compared with controls. These phenotypes could be rescued by co-injection of human wild-type SHROOM4 mRNA and morpholino.
Conclusion: The identified SNVs and CNVs in affected individuals with congenital anomalies of the urinary tract, the anorectal, the cardiovascular and the central nervous systems, and subsequent embryonic mouse and zebrafish studies suggest SHROOM4 as a developmental gene for different organ systems.
Keywords: congenital, hereditary, and neonatal diseases and abnormalities; digestive system abnormalities; genetic counseling; heart defects, congenital; nervous system malformations.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rare copy number variants analysis identifies novel candidate genes in heterotaxy syndrome patients with congenital heart defects.Genome Med. 2018 May 30;10(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13073-018-0549-y. Genome Med. 2018. PMID: 29843777 Free PMC article.
-
SHROOM4 Variants Are Associated With X-Linked Epilepsy With Features of Generalized Seizures or Generalized Discharges.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 May 17;15:862480. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.862480. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35663265 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of copy number disorders associated with congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract in fetuses via single nucleotide polymorphism arrays.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jan;34(1):e23025. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23025. Epub 2019 Sep 10. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 31506986 Free PMC article.
-
Obstetrical Outcomes in Adult Patients Born with Complex Anorectal Malformations and Cloacal Anomalies: A Literature Review.J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2019 Feb;32(1):7-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 24. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2019. PMID: 30367985 Review.
-
Congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract--role of the loss of function mutation in the pluripotent angiotensin type 2 receptor gene.J Urol. 2001 Jan;165(1):196-202. doi: 10.1097/00005392-200101000-00057. J Urol. 2001. PMID: 11125405 Review.
Cited by
-
Modelling human lower urinary tract malformations in zebrafish.Mol Cell Pediatr. 2023 Mar 29;10(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s40348-023-00156-4. Mol Cell Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36977792 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stocco dos Santos RC, Castro NHC, Lillia Holmes A, Beçak W, Tackels-Horne D, Lindsey CJ, Lubs HA, Stevenson RE, Schwartz CE, Holmes AL. Stocco DOS Santos X-linked mental retardation syndrome: clinical elucidation and localization to Xp11.3-Xq21.3. Am J Med Genet A 2003;118A:255–9. 10.1002/ajmg.a.20021 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hagens O, Dubos A, Abidi F, Barbi G, Van Zutven L, Hoeltzenbein M, Tommerup N, Moraine C, Fryns J-P, Chelly J, van Bokhoven H, Gécz J, Dollfus H, Ropers H-H, Schwartz CE, de Cassia Stocco Dos Santos R, Kalscheuer V, Hanauer A. Disruptions of the novel KIAA1202 gene are associated with X-linked mental retardation. Hum Genet 2006;118:578–90. 10.1007/s00439-005-0072-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
