A single center analysis of first-line treatment in advanced KRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer: real-world practice
- PMID: 36376839
- PMCID: PMC9664628
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-10236-9
A single center analysis of first-line treatment in advanced KRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer: real-world practice
Abstract
Purpose: For the first-line treatment of KRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, immunotherapy or platinum-based chemotherapy are the main treatment method. Here, we investigated the clinical efficacy and prognosis those two regimens as first-line treatment in real-world practice.
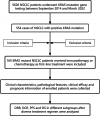
Methods: KRAS mutant NSCLC patients received chemotherapy or immunotherapy as first-line treatment from September 2014 to March 2022 were enrolled. Clinical characteristics, treatment scheme, clinical curative effect and follow-up data of enrolled patients were collected for analysis.
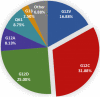
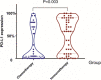
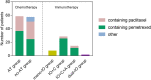
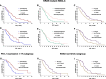
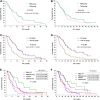
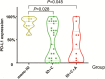
Results: Fifty patients received immunotherapy and 115 patients received chemotherapy were enrolled. Patients who received immunotherapy (HR = 0.350, 95%CI 0.156-0.781, P = 0.010), or pemetrexed-based regimen (HR = 0.486, 95%CI 0.255-0.928, P = 0.029), or antiangiogenic therapy (HR = 0.355, 95%CI 0.159-0.790, P = 0.011) were at a low risk of disease progression. And patients received antiangiogenic therapy had lower risk of death than those not (HR = 0.333, 95%CI 0.120-0.926, P = 0.035). Subgroup analysis revealed the immunotherapy compared to chemotherapy alone had lower risk of disease progression (HR = 0.377, 95%CI 0.166-0.856, P = 0.020) in PD-L1 expression ≥1% subgroup. And in non-G12C KRAS subgroup, but not in G12C KRAS subgroup, patients who received antiangiogenic therapy had lower risk of disease progression (HR = 0.254, 95%CI 0.098-0.656, P = 0.005) and death than those not (HR = 0.197, 95%CI 0.056-0.692, P = 0.011). In terms of different chemotherapy regimen, platinum-paclitaxel combined with antiangiogenic therapy achieved the highest ORR and DCR (P < 0.05), while the platinum-pemetrexed combined with antiangiogenic therapy had the longest PFS and OS (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: For the first-line treatment of KRAS mutant NSCLC patients, immunotherapy, antiangiogenic therapy, and pemetrexed-based regimen could obtain more benefits. Subgroup analysis revealed the benefits of immunotherapy compared to chemotherapy were applicable in PD-L1 expression≥1% subgroup, and antiangiogenic therapy could benefit non-G12C KRAS subgroup, but not G12C KRAS subgroup. In terms of different chemotherapy regimen, platinum-pemetrexed combined with antiangiogenic therapy may be the preferred chemotherapy regimen.
Keywords: Antiangiogenic therapy; First-line treatment; Immunotherapy; KRAS mutation; NSCLC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical outcomes to pemetrexed-based versus non-pemetrexed-based platinum doublets in patients with KRAS-mutant advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2020 May;22(5):708-716. doi: 10.1007/s12094-019-02175-y. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Clin Transl Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31332704
-
The prevalence and real-world therapeutic analysis of Chinese patients with KRAS-Mutant Non-Small Cell lung cancer.Cancer Med. 2022 Oct;11(19):3581-3592. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4739. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35394121 Free PMC article.
-
A Multicenter Retrospective Chart Review of Clinical Outcomes Among Patients With KRAS G12C Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Clin Lung Cancer. 2023 May;24(3):228-234. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2023.01.009. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Clin Lung Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36841727 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors vs. Chemotherapy for KRAS-Mutant or EGFR-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancers: A Meta-Analysis Based on Randomized Controlled Trials.Dis Markers. 2022 Aug 26;2022:2631852. doi: 10.1155/2022/2631852. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 36061356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sintilimab plus chemotherapy for first-line treatment of advanced or metastatic nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer: network meta-analysis.Immunotherapy. 2023 Mar;15(4):293-309. doi: 10.2217/imt-2022-0252. Epub 2023 Feb 7. Immunotherapy. 2023. PMID: 36748406 Review.
Cited by
-
Exceptionally long-lasting response to dabrafenib plus trametinib treatment in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma harboring the BRAF V600E mutation with high expression of PD-L1: A case report.Thorac Cancer. 2024 Apr;15(11):929-933. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.15254. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Thorac Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38429896 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Applications of Comprehensive Genomic Profiling in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer-A Case Series.Curr Oncol. 2024 May 31;31(6):3161-3176. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31060239. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38920723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg SB, Schlessinger J, Boyer JL, Herbst RS. A step towards treating KRAS-mutant NSCLC. The Lancet Oncology. 2013;14(1):3–5. - PubMed
-
- Jordan EJ, Kim HR, Arcila ME, Barron D, Chakravarty D, Gao J, Chang MT, Ni A, Kundra R, Jonsson P, et al. Prospective comprehensive molecular characterization of lung adenocarcinomas for efficient patient matching to approved and emerging therapies. Cancer discovery. 2017;7(6):596–609. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kranenburg O. The KRAS oncogene: past, present, and future. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1756(2):81–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

