The developmental trajectories of the behavioral phenotype and neuropsychiatric functioning in Cornelia de Lange and Rubinstein Taybi syndromes: A longitudinal study
- PMID: 36373849
- PMCID: PMC10099472
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.63039
The developmental trajectories of the behavioral phenotype and neuropsychiatric functioning in Cornelia de Lange and Rubinstein Taybi syndromes: A longitudinal study
Abstract
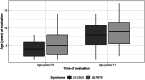
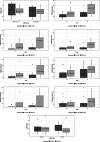
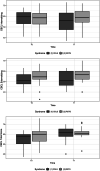
Several changes in the behavioral phenotype arise with the growth of children affected by Cornelia de Lange Syndrome (CdLS) and Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome (RSTS). However, previous research relied on a cross-sectional study design turning into age-related comparisons of different syndromic cohorts to explore age-dependent changes. We aim to outline the variating pathways of the neuropsychiatric functioning across the lifespan in CdLS and RSTS, through the setting up of a longitudinal study design. The sample included 14 patients with CdLS and 15 with RSTS. The assessments were carried out in two different timepoints. Our findings highlight that the cognitive profile of CdLS is subjected to a worsening trend with decreasing Intellectual Quotient (IQ) scores from T0 to T1, whereas RSTS shows a stable IQ over time. Patients affected by RSTS show greater improvements compared to CdLS in communication, daily living skills, social abilities, and motor skills across the lifespan. Both syndromes report an upward trend in behavioral and emotional difficulties even if CdLS exhibit a significant and major deterioration compared to individuals with RSTS. Being aware of the early dysfunctional patterns which might pave the way for later neuropsychiatric impairments is the first step for planning preventive interventions.
Keywords: CdLS; RSTS; behavioral phenotype; intellectual disability; longitudinal assessment; rehabilitation.
© 2022 The Authors. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Age-related hallmarks of psychopathology in Cornelia de Lange and Rubinstein-Taybi syndromes.Res Dev Disabil. 2022 Jul;126:104235. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2022.104235. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Res Dev Disabil. 2022. PMID: 35468572
-
The development of early social cognitive skills in neurogenetic syndromes associated with autism: Cornelia de Lange, fragile X and Rubinstein-Taybi syndromes.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021 Nov 22;16(1):488. doi: 10.1186/s13023-021-02117-4. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021. PMID: 34809685 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Profiles of Anxiety Related Disorders in Fragile X, Cornelia de Lange and Rubinstein-Taybi Syndromes.J Autism Dev Disord. 2017 Dec;47(12):3728-3740. doi: 10.1007/s10803-016-3015-y. J Autism Dev Disord. 2017. PMID: 28144878 Free PMC article.
-
Exome sequencing identifies a novel EP300 frame shift mutation in a patient with features that overlap Cornelia de Lange syndrome.Am J Med Genet A. 2014 Jan;164A(1):251-8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36237. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Am J Med Genet A. 2014. PMID: 24352918 Review.
-
Behavioral markers of social anxiety in Cornelia de Lange Syndrome: A brief systematic review.J Affect Disord. 2022 Feb 15;299:636-643. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.12.099. Epub 2021 Dec 23. J Affect Disord. 2022. PMID: 34953928 Review.
References
-
- Achenbach, T. M. , Dumenci, L. , & Rescorla, L. A. (2001). Ratings of relations between DSM‐IV diagnostic categories and items of the CBCL/6–18, TRF, and YSR. University of Vermont.
-
- Ajmone, P. F. , Allegri, B. , Cereda, A. , Michelini, G. , Dall'Ara, F. , Mariani, M. , Rigamonti, C. , Selicorni, A. , Vizziello, P. , & Costantino, M. A. (2021). Neuropsychiatric functioning in CDLS: A detailed phenotype and genotype correlation. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 52, 4763–4773. 10.1007/s10803-021-05343-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ajmone, P. F. , Avignone, S. , Gervasini, C. , Giacobbe, A. , Monti, F. , Costantino, A. , Esposito, S. , Marchisio, P. , Triulzi, F. , & Milani, D. (2018). Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: New neuroradiological and neuropsychiatric insights from a multidisciplinary approach. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 177(4), 406–415. 10.1002/ajmg.b.32628 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ajmone, P. F. , Rigamonti, C. , Dall'Ara, F. , Monti, F. , Vizziello, P. , Milani, D. , Cereda, A. , Selicorni, A. , & Costantino, A. (2014). Communication, cognitive development and behavior in children with Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS): Preliminary results. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 165(3), 223–229. 10.1002/ajmg.b.32224 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials