Membrane phosphoinositides regulate GPCR-β-arrestin complex assembly and dynamics
- PMID: 36368322
- PMCID: PMC10030194
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.10.018
Membrane phosphoinositides regulate GPCR-β-arrestin complex assembly and dynamics
Abstract
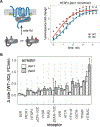
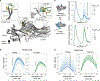
Binding of arrestin to phosphorylated G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) is crucial for modulating signaling. Once internalized, some GPCRs remain complexed with β-arrestins, while others interact only transiently; this difference affects GPCR signaling and recycling. Cell-based and in vitro biophysical assays reveal the role of membrane phosphoinositides (PIPs) in β-arrestin recruitment and GPCR-β-arrestin complex dynamics. We find that GPCRs broadly stratify into two groups, one that requires PIP binding for β-arrestin recruitment and one that does not. Plasma membrane PIPs potentiate an active conformation of β-arrestin and stabilize GPCR-β-arrestin complexes by promoting a fully engaged state of the complex. As allosteric modulators of GPCR-β-arrestin complex dynamics, membrane PIPs allow for additional conformational diversity beyond that imposed by GPCR phosphorylation alone. For GPCRs that require membrane PIP binding for β-arrestin recruitment, this provides a mechanism for β-arrestin release upon translocation of the GPCR to endosomes, allowing for its rapid recycling.
Keywords: GPCR; arrestin; conformational dynamics; endocytosis; fluorescence spectroscopy; phosphoinositides; signaling.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests B.K.K. is a cofounder and consultant for ConfometRx, Inc.
Figures




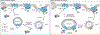
Similar articles
-
β-arrestins and G protein-coupled receptor trafficking.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;219:173-86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-41199-1_9. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24292830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-arrestin-dependent PI(4,5)P2 synthesis boosts GPCR endocytosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Apr 27;118(17):e2011023118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2011023118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33879605 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction at GPCRs: Allosteric activation of the ERK MAPK by β-arrestin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Oct 24;120(43):e2303794120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2303794120. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37844230 Free PMC article.
-
Catalytic activation of β-arrestin by GPCRs.Nature. 2018 May;557(7705):381-386. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0079-1. Epub 2018 May 2. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29720660 Free PMC article.
-
β-Arrestins and G protein-coupled receptor trafficking.Methods Enzymol. 2013;521:91-108. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-391862-8.00005-3. Methods Enzymol. 2013. PMID: 23351735 Review.
Cited by
-
Location-biased β-arrestin conformations direct GPCR signaling.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 26:2024.09.24.614742. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.24.614742. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39386521 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Computational drug development for membrane protein targets.Nat Biotechnol. 2024 Feb;42(2):229-242. doi: 10.1038/s41587-023-01987-2. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Nat Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38361054 Review.
-
Superior performance of biocomposite nanoparticles PLGA-RES in protecting oocytes against vitrification stimuli.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Mar 11;12:1376205. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1376205. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38529403 Free PMC article.
-
Control of G protein-coupled receptor function via membrane-interacting intrinsically disordered C-terminal domains.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 16;121(29):e2407744121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2407744121. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38985766 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of β-arrestin-2 pre-activation by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate.EMBO Rep. 2024 Oct;25(10):4190-4205. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00239-x. Epub 2024 Sep 6. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 39242774 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

