A Review of Radiation-Induced Alterations of Multi-Omic Profiles, Radiation Injury Biomarkers, and Countermeasures
- PMID: 36368026
- PMCID: PMC10279411
- DOI: 10.1667/RADE-21-00187.1
A Review of Radiation-Induced Alterations of Multi-Omic Profiles, Radiation Injury Biomarkers, and Countermeasures
Abstract
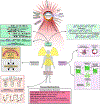
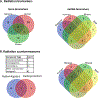
Increasing utilization of nuclear power enhances the risks associated with industrial accidents, occupational hazards, and the threat of nuclear terrorism. Exposure to ionizing radiation interferes with genomic stability and gene expression resulting in the disruption of normal metabolic processes in cells and organs by inducing complex biological responses. Exposure to high-dose radiation causes acute radiation syndrome, which leads to hematopoietic, gastrointestinal, cerebrovascular, and many other organ-specific injuries. Altered genomic variations, gene expression, metabolite concentrations, and microbiota profiles in blood plasma or tissue samples reflect the whole-body radiation injuries. Hence, multi-omic profiles obtained from high-resolution omics platforms offer a holistic approach for identifying reliable biomarkers to predict the radiation injury of organs and tissues resulting from radiation exposures. In this review, we performed a literature search to systematically catalog the radiation-induced alterations from multi-omic studies and radiation countermeasures. We covered radiation-induced changes in the genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, metabolomic, lipidomic, and microbiome profiles. Furthermore, we have covered promising multi-omic biomarkers, FDA-approved countermeasure drugs, and other radiation countermeasures that include radioprotectors and radiomitigators. This review presents an overview of radiation-induced alterations of multi-omics profiles and biomarkers, and associated radiation countermeasures.
© 2023 by Radiation Research Society. All rights of reproduction in any form reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel biomarkers for acute radiation injury and countermeasures using large and small animal models and multi-omics approach.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2023 Sep 18;199(14):1526-1532. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncad035. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2023. PMID: 37721071
-
Medical countermeasures for unwanted CBRN exposures: part II radiological and nuclear threats with review of recent countermeasure patents.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2016 Dec;26(12):1399-1408. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2016.1231805. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2016. PMID: 27610458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein biomarkers for radiation injury and testing of medical countermeasure efficacy: promises, pitfalls, and future directions.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2023 Jul-Dec;20(10):221-246. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2023.2263652. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 37752078 Review.
-
Ionizing radiation-induced altered microRNA expression as biomarkers for assessing acute radiation injury.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2017 Oct;17(10):871-874. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2017.1366316. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2017. PMID: 28792262 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
A Metabolomic Serum Signature from Nonhuman Primates Treated with a Radiation Countermeasure, Gamma-tocotrienol, and Exposed to Ionizing Radiation.Health Phys. 2018 Jul;115(1):3-11. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000000776. Health Phys. 2018. PMID: 29787425 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ionizing Radiation Dose Differentially Affects the Host-Microbe Relationship over Time.Microorganisms. 2024 Sep 30;12(10):1995. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12101995. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39458305 Free PMC article.
-
Development of radiation countermeasure agents for acute radiation syndromes.Animal Model Exp Med. 2023 Aug;6(4):329-336. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12339. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Animal Model Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37642199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early and long-term responses of intestinal microbiota and metabolites to 131I treatment in differentiated thyroid cancer patients.BMC Med. 2024 Jul 18;22(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03528-3. BMC Med. 2024. PMID: 39020393 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-species conserved miRNA as biomarker of radiation injury over a wide dose range using nonhuman primate model.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 21;19(11):e0311379. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311379. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39570918 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombopoietin mimetic stimulates bone marrow vascular and stromal niches to mitigate acute radiation syndrome.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Apr 29;15(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03734-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38679747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- !!! INVALID CITATION !!! (2).
-
- Oh YJ, Kwak MS, Sung MH, Protection of Radiation-Induced DNA Damage by Functional Cosmeceutical Poly-Gamma-Glutamate. J Microbiol Biotechnol 2018; 28, 527–33. - PubMed
-
- Santivasi WL, Xia F, Ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage, response, and repair. Antioxid Redox Signal 2014; 21, 251–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

