Immunoinformatics-Aided Design of a Peptide Based Multiepitope Vaccine Targeting Glycoproteins and Membrane Proteins against Monkeypox Virus
- PMID: 36366472
- PMCID: PMC9693848
- DOI: 10.3390/v14112374
Immunoinformatics-Aided Design of a Peptide Based Multiepitope Vaccine Targeting Glycoproteins and Membrane Proteins against Monkeypox Virus
Abstract
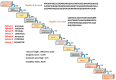
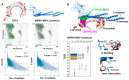
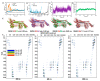
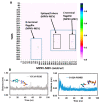
Monkeypox is a self-limiting zoonotic viral disease and causes smallpox-like symptoms. The disease has a case fatality ratio of 3-6% and, recently, a multi-country outbreak of the disease has occurred. The currently available vaccines that have provided immunization against monkeypox are classified as live attenuated vaccinia virus-based vaccines, which pose challenges of safety and efficacy in chronic infections. In this study, we have used an immunoinformatics-aided design of a multi-epitope vaccine (MEV) candidate by targeting monkeypox virus (MPXV) glycoproteins and membrane proteins. From these proteins, seven epitopes (two T-helper cell epitopes, four T-cytotoxic cell epitopes and one linear B cell epitopes) were finally selected and predicted as antigenic, non-allergic, interferon-γ activating and non-toxic. These epitopes were linked to adjuvants to design a non-allergic and antigenic candidate MPXV-MEV. Further, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations predicted stable interactions between predicted MEV and human receptor TLR5. Finally, the immune-simulation analysis showed that the candidate MPXV-MEV could elicit a human immune response. The results obtained from these in silico experiments are promising but require further validation through additional in vivo experiments.
Keywords: epitope-based vaccine; immunoinformatics; monkeypox; monkeypox virus; orthopoxvirus; reverse vaccinology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Authors R.K.G. and A.R.S. were employed by the company STEMskills Research and Education Lab Private Limited, Faridabad, Haryana, India. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multi-epitope chimeric vaccine design against emerging Monkeypox virus via reverse vaccinology techniques- a bioinformatics and immunoinformatics approach.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 25;13:985450. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.985450. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36091024 Free PMC article.
-
In silico designing a novel TLR4-mediating multiepitope vaccine against monkeypox via advanced immunoinformatics and bioinformatics approaches.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Feb-Mar;42(4):2094-2110. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2203253. Epub 2023 May 2. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37129119
-
Immunoinformatic-guided novel mRNA vaccine designing to elicit immunogenic responses against the endemic Monkeypox virus.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Aug;42(12):6292-6306. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2233627. Epub 2023 Jul 9. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37424185
-
Current Status of Vaccine Development for Monkeypox Virus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1451:289-300. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-57165-7_18. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38801585 Review.
-
Reverse engineering protection: A comprehensive survey of reverse vaccinology-based vaccines targeting viral pathogens.Vaccine. 2024 Apr 11;42(10):2503-2518. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.02.087. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Vaccine. 2024. PMID: 38523003 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunoinformatics and reverse vaccinology approach in designing a novel highly immunogenic multivalent peptide-based vaccine against the human monkeypox virus.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Nov 22;10:1295817. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1295817. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38074091 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoinformatics-aided rational design of a multi-epitope vaccine targeting feline infectious peritonitis virus.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Dec 13;10:1280273. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1280273. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38192725 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoinformatics and computational approaches driven designing a novel vaccine candidate against Powassan virus.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 12;14(1):5999. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56554-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38472237 Free PMC article.
-
Universal peptide-based potential vaccine design against canine distemper virus (CDV) using a vaccinomic approach.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 18;14(1):16605. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67781-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39026076 Free PMC article.
-
Secreted Aspartyl Proteinases Targeted Multi-Epitope Vaccine Design for Candida dubliniensis Using Immunoinformatics.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Feb 5;11(2):364. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020364. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851241 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

