Blood Center Testing Allows the Detection and Rapid Treatment of Acute and Recent HIV Infection
- PMID: 36366424
- PMCID: PMC9698357
- DOI: 10.3390/v14112326
Blood Center Testing Allows the Detection and Rapid Treatment of Acute and Recent HIV Infection
Abstract
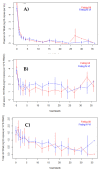
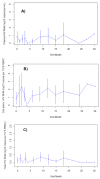
Blood donations in South Africa are tested for HIV RNA using individual donation NAT (ID-NAT), allowing detection and rapid antiretroviral therapy (ART) of acute HIV infections. We enrolled a cohort of acute and recent HIV-infected blood donation candidates in South Africa in 2015-2018, measured HIV antibody, ID-NAT, and recency of infection <195 days (Sedia LAg) at enrollment and initiated early ART. A small cohort of HIV elite controllers was followed without treatment. HIV reservoir measurements included ultrasensitive plasma RNA, cell-associated HIV RNA, and total DNA. Enrollment of 18 Fiebig I-III and 45 Fiebig IV-VI HIV clade C subjects occurred a median of 18 days after index blood donation. ART was administered successfully and compliance with follow-up visits was excellent. There were only minimal differences in HIV reservoir between ART initiation in Fiebig stages I-III vs. IV-VI, but ART noncompliance increased HIV reservoir. In 11 untreated HIV elite controllers, HIV reservoir levels were similar to or higher than those seen in our early treated cohort. National blood services can identify acute HIV cohorts for subsequent HIV cure research studies. Among HIV clade C-infected donors, HIV reservoir differed little by Fiebig stage at treatment initiation, but was smaller than in chronically treated HIV and those with ART noncompliance.
Keywords: HIV clade C; HIV cure; HIV reservoir; South Africa; blood donors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Viral kinetics in untreated versus treated acute HIV infection in prospective cohort studies in Thailand.J Int AIDS Soc. 2017 Jun 26;20(1):21652. doi: 10.7448/IAS.20.1.21652. J Int AIDS Soc. 2017. PMID: 28691436 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and treatment of Fiebig stage I HIV-1 infection in young at-risk women in South Africa: a prospective cohort study.Lancet HIV. 2018 Jan;5(1):e35-e44. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(17)30146-7. Epub 2017 Oct 1. Lancet HIV. 2018. PMID: 28978417 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid development of HIV elite control in a patient with acute infection.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Sep 18;19(1):815. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4374-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31533639 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of HIV-1 reservoir size and broadly neutralizing antibody susceptibility in acute antiretroviral therapy-treated individuals.AIDS. 2022 Feb 1;36(2):205-214. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000003088. AIDS. 2022. PMID: 34586088
-
HIV-1 persistence following extremely early initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART) during acute HIV-1 infection: An observational study.PLoS Med. 2017 Nov 7;14(11):e1002417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002417. eCollection 2017 Nov. PLoS Med. 2017. PMID: 29112956 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Viruses Special Issue "Transfusion-Transmitted Viral Infections".Viruses. 2022 Dec 28;15(1):86. doi: 10.3390/v15010086. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36680126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henrich T.J., Hatano H., Bacon O., Hogan L.E., Rutishauser R., Hill A., Kearney M., Anderson E.M., Buchbinder S.P., Cohen S.E., et al. HIV-1 persistence following extremely early initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART) during acute HIV-1 infection: An observational study. PLoS Med. 2017;14:e1002417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002417. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Muccini C., Crowell T.A., Kroon E., Sacdalan C., Ramautarsing R., Seekaew P., Phanuphak P., Ananworanich J., Colby D.J., Phanuphaket N. Leveraging early HIV diagnosis and treatment in Thailand to conduct HIV cure research. AIDS Res. Ther. 2019;16:25. doi: 10.1186/s12981-019-0240-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

