Laboratory Indicators for Identifying Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36366337
- PMCID: PMC9694715
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10111829
Laboratory Indicators for Identifying Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study is to study laboratory indicators for the identification of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) severity.
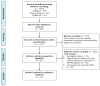
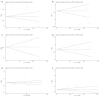
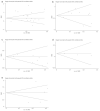
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, and the Web of Science for literature that was published before May 2022. The main results are presented as forest plots. Subgroup analyses, sensitivity analyses, and publication bias were also performed.
Results: Our study indicated that white blood cells (WBC) (95%CI: 0.205-0.778), blood glucose (95%CI: 0.505-0.778), lymphocytes (95%CI: 0.072-0.239), creatinine (95%CI: 0.024-0.228), interleukin (IL)-2 (95%CI: 0.192-1.642), IL-6 (95%CI: 0.289-0.776), IL-8 (95%CI: 0.499-0.867), IL-10 (95%CI: 0.226-0.930), interferon-γ (IFN-γ) (95%CI: 0.193-2.584), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (95%CI: 1.078-2.715), and creatine kinase MB isoenzyme (CK-MB) (95%CI: 0.571-1.459) were associated with an increased risk of HFMD severity, and the results of the sensitivity analysis of these indicators were stable and free of publication bias.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that various deleterious immune and metabolic changes can increase the risk of HFMD severity, which can provide a basis for predicting the prognosis and useful evidence for clinicians to manage patients efficiently.
Keywords: hand, foot and mouth disease; laboratory indicators; meta-analysis; severity; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Epidemiological characteristics, routine laboratory diagnosis, clinical signs and risk factors for hand, -foot -and -mouth disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 28;17(4):e0267716. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267716. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35482791 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Meteorological Parameters and Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in Mainland China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2021 Sep;50(9):1757-1765. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v50i9.7046. Iran J Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34722370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The characteristics of blood glucose and WBC counts in peripheral blood of cases of hand foot and mouth disease in China: a systematic review.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29003. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029003. Epub 2012 Jan 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22235257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum inflammatory cytokine levels correlate with hand-foot-mouth disease severity: a nested serial case-control study.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 12;9(11):e112676. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112676. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25391156 Free PMC article.
-
Increased effector γδ T cells with enhanced cytokine production are associated with inflammatory abnormalities in severe hand, foot, and mouth disease.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Aug;73:172-180. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.067. Epub 2019 May 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31100712
Cited by
-
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Challenges and Its Antiviral Therapeutics.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Mar 1;11(3):571. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11030571. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36992155 Free PMC article.
-
Diaper dermatitis-a narrative review of clinical presentation, subtypes, and treatment.Wien Med Wochenschr. 2024 Sep;174(11-12):246-256. doi: 10.1007/s10354-023-01024-6. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2024. PMID: 37861874 Review. English.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 82002147/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82073618/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2019M662543/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- 20A330004/Key Scientific Research Project of Henan Institution of Higher Education
- 21A310026/Key Scientific Research Project of Henan Institution of Higher Education
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

