Structural Investigation of Betulinic Acid Plasma Metabolites by Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 36364186
- PMCID: PMC9656950
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27217359
Structural Investigation of Betulinic Acid Plasma Metabolites by Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
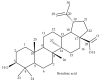
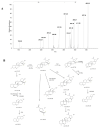
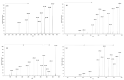
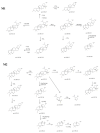
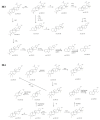
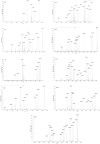
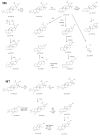
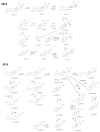
Betulinic acid (BA) has been extensively studied in recent years mainly for its antiproliferative and antitumor effect in various types of cancers. Limited data are available regarding the pharmacokinetic profile of BA, particularly its metabolic transformation in vivo. In this study, we present the screening and structural investigations by ESI Orbitrap MS in the negative ion mode and CID MS/MS of phase I and phase II metabolites detected in mouse plasma after the intraperitoneal administration of a nanoemulsion containing BA in SKH 1 female mice. Obtained results indicate that the main phase I metabolic reactions that BA undergoes are monohydroxylation, dihydroxylation, oxidation and hydrogenation, while phase II reactions involved sulfation, glucuronidation and methylation. The fragmentation pathway for BA and its plasma metabolites were elucidated by sequencing of the precursor ions by CID MS MS experiments.
Keywords: ESI CID MS/MS; betulinic acid; phase I metabolites; phase II metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quantitative analysis of betulinic acid in mouse, rat and dog plasma using electrospray liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2003;17(18):2089-92. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1155. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2003. PMID: 12955738
-
In vivo metabolic investigation of moxifloxacin using liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry in combination with online hydrogen/deuterium exchange experiments.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2012 Aug 30;26(16):1817-31. doi: 10.1002/rcm.6288. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2012. PMID: 22777784
-
Identification and structural characterization of in vivo metabolites of balofloxacin in rat plasma, urine and feces samples using Q-TOF/LC/ESI/MS/MS : In silico toxicity studies.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Sep 10;159:200-211. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.06.050. Epub 2018 Jun 28. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29990887
-
In vivo and in vitro metabolism and pharmacokinetics of cholinesterase inhibitor deoxyvasicine from aerial parts of Peganum harmala Linn in rats via UPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS and UPLC-ESI-MS/MS.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 May 23;236:288-301. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.03.020. Epub 2019 Mar 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30872168
-
Metabolic profiles and pharmacokinetics of picroside I in rats by liquid chromatography combined with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2018 Sep 15;1095:157-165. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.07.034. Epub 2018 Jul 29. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 30077096
Cited by
-
Cytotoxic activity of Fomitopsis betulina against normal and cancer cells - a comprehensive literature review.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2024;28(3):191-200. doi: 10.5114/wo.2024.144223. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2024. PMID: 39512529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Betulinic Acid Hydroxamate in Intraventricular Hemorrhage-Induced Brain Damage in Immature Rats.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 12;14(24):5286. doi: 10.3390/nu14245286. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36558445 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic Potential of Betulinic Acid Fatty Esters and Their Liposomal Formulations: Targeting Breast, Colon, and Lung Cancer Cell Lines.Molecules. 2024 Jul 19;29(14):3399. doi: 10.3390/molecules29143399. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39064977 Free PMC article.
-
Euonymus alatus (Thunb.) Siebold Prevents Osteoclast Differentiation and Osteoporosis.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 15;15(18):3996. doi: 10.3390/nu15183996. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karan B.N., Maity T.K., Pal B.C., Singha T., Jana S. Betulinic Acid, the first lupane-type triterpenoid isolated via bioactivity-guided fractionation, and identified by spectroscopic analysis from leaves of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis: Its potential biological activities in vitro assays. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019;33:3287–3292. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2018.1470171. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hordyjewska A., Ostapiuk A., Horecka A., Kurzepa J. Betulin and betulinic acid: Triterpenoids derivatives with a powerful biological potential. Phytochem. Rev. 2019;18:929–951. doi: 10.1007/s11101-019-09623-1. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

