The Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha in Renal Disease
- PMID: 36364144
- PMCID: PMC9657345
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27217318
The Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha in Renal Disease
Abstract
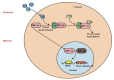
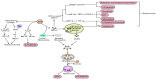
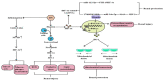
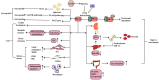
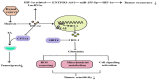
Partial pressure of oxygen (pO2) in the kidney is maintained at a relatively stable level by a unique and complex functional interplay between renal blood flow, glomerular filtration rate (GFR), oxygen consumption, and arteriovenous oxygen shunting. The vulnerability of this interaction renders the kidney vulnerable to hypoxic injury, leading to different renal diseases. Hypoxia has long been recognized as an important factor in the pathogenesis of acute kidney injury (AKI), especially renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Accumulating evidence suggests that hypoxia also plays an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and CKD-related complications, such as anemia, cardiovascular events, and sarcopenia. In addition, renal cancer is linked to the deregulation of hypoxia pathways. Renal cancer utilizes various molecular pathways to respond and adapt to changes in renal oxygenation. Particularly, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) (including HIF-1, 2, 3) has been shown to be activated in renal disease and plays a major role in the protective response to hypoxia. HIF-1 is a heterodimer that is composed of an oxygen-regulated HIF-1α subunit and a constitutively expressed HIF-1β subunit. In renal diseases, the critical characteristic of HIF-1α is protective, but it also has a negative effect, such as in sarcopenia. This review summarizes the mechanisms of HIF-1α regulation in renal disease.
Keywords: complications; diabetic nephropathy; hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; renal cancer; renal ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Silencing of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α gene attenuates chronic ischemic renal injury in two-kidney, one-clip rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 May 15;306(10):F1236-42. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00673.2013. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24623146 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α activation improves renal oxygenation and mitochondrial function in early chronic kidney disease.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Aug 1;313(2):F282-F290. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00579.2016. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28331062 Free PMC article.
-
FIH-1-modulated HIF-1α C-TAD promotes acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease progression via regulating KLF5 signaling.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Dec;42(12):2106-2119. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00617-4. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 33658705 Free PMC article.
-
The role of hypoxia, increased oxygen consumption, and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in progression of chronic kidney disease.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010 Jan;19(1):43-50. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e3283328eed. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010. PMID: 19779337 Review.
-
Mechanisms Leading to Differential Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Signaling in the Diabetic Kidney: Modulation by SGLT2 Inhibitors and Hypoxia Mimetics.Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Feb;77(2):280-286. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.04.016. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 32711072 Review.
Cited by
-
Injectable Microparticle-containing hydrogel with controlled release of bioactive molecules for facial rejuvenation.Mater Today Bio. 2023 Dec 1;24:100890. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100890. eCollection 2024 Feb. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 38162281 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of renal hemodynamics and functions by Nigella sativa administration in dinitrophenol-induced hypoxia in rat's animal model.Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2024 Jul-Aug;18(4):22-31. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2024. PMID: 38974646 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN in kidney diseases: a potential therapeutic target in preventing AKI-to-CKD transition.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 6;11:1428995. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1428995. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39165377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxic Inducible Factor Stabilization in Pericytes beyond Erythropoietin Production: The Good and the Bad.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 27;13(5):537. doi: 10.3390/antiox13050537. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy and its therapeutic potential in diabetic nephropathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 20;14:1139444. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1139444. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37020591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

