LMNA Reduced Acquired Resistance to Erlotinib in NSCLC by Reversing the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via the FGFR/MAPK/c-fos Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 36362025
- PMCID: PMC9658955
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232113237
LMNA Reduced Acquired Resistance to Erlotinib in NSCLC by Reversing the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via the FGFR/MAPK/c-fos Signaling Pathway
Abstract
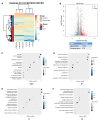
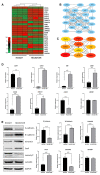
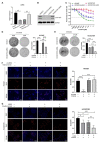
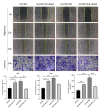
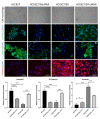
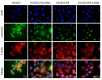
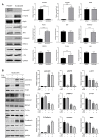
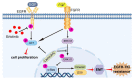
For patients exhibiting non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with activating epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) are a first-line treatment. However, most patients who initially responded to EGFR-TKIs eventually developed acquired resistance, limiting the effectiveness of therapy. It has long been known that epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) leads to acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs in NSCLC. However, the mechanisms underlying the resistance dependent on EMT are unknown. This research aimed to reveal the effects of LMNA in the regulation of acquired resistance to erlotinib by EMT in NSCLC. The acquired erlotinib-resistant cells (HCC827/ER) were induced by gradual increase of concentrations of erlotinib in erlotinib-sensitive HCC827 cells. RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis were performed to uncover the involvement of LMNA in the EMT process that induced acquired resistance to erlotinib. The effect of LMNA on cell proliferation and migration was measured by clone-formation, wound-healing, and transwell assays, respectively. The EMT-related protein, nuclear shape and volume, and cytoskeleton changes were examined by immunofluorescence. Western blot was used to identify the underlying molecular mechanism of LMNA regulation of EMT. HCC827/ER cells with acquired resistance to erlotinib underwent EMT and exhibited lower LMNA expression compared to parental sensitive cells. LMNA negatively regulated the expression of EMT markers; HCC827/ER cells showed a significant up-regulation of mesenchymal markers, such as CDH2, SNAI2, VIM, ZEB1, and TWIST1. The overexpression of LMNA in HCC827/ER cells significantly inhibited EMT and cell proliferation, and this inhibitory effect of LMNA was enhanced in the presence of 2.5 μM erlotinib. Furthermore, a decrease in LMNA expression resulted in a higher nuclear deformability and cytoskeletal changes. In HCC827/ER cells, AKT, FGFR, ERK1/2, and c-fos phosphorylation levels were higher than those in HCC827 cells; Furthermore, overexpression of LMNA in HCC827/ER cells reduced the phosphorylation of AKT, ERK1/2, c-fos, and FGFR. In conclusion, our findings first demonstrated that downregulation of LMNA promotes acquired EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC with EGFR mutations by EMT. LMNA inhibits cell proliferation and migration of erlotinib-resistant cells via inhibition of the FGFR/MAPK/c-fos signaling pathway. These findings indicated LMNA as a driver of acquired resistance to erlotinib and provided important information about the development of resistance to erlotinib treatment in NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations.
Keywords: EGFR-TKI resistance; LMNA; epithelial–mesenchymal transition; non-small-cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polyphyllin I Overcomes EMT-Associated Resistance to Erlotinib in Lung Cancer Cells via IL-6/STAT3 Pathway Inhibition.Biol Pharm Bull. 2017 Aug 1;40(8):1306-1313. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b17-00271. Epub 2017 May 18. Biol Pharm Bull. 2017. PMID: 28515374
-
IGF1R depletion facilitates MET-amplification as mechanism of acquired resistance to erlotinib in HCC827 NSCLC cells.Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(20):33300-33315. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16350. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28418902 Free PMC article.
-
[Molecular mechanism of erlotinib resistance in epidermal growth factor receptor mutant non-small cell lung cancer cell line H1650].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2012 Dec;15(12):689-93. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2012.12.02. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23249714 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway.Clin Lung Cancer. 2009 Jul;10(4):281-9. doi: 10.3816/CLC.2009.n.039. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19632948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research Progress of the Role of EMT in EGFR-TKIs Resistance of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018 Dec 20;21(12):907-911. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2018.12.08. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30591098 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The Multifaceted Roles of Lamins in Lung Cancer and DNA Damage Response.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 21;15(23):5501. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235501. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N4-acetylcytidine modifies primary microRNAs for processing in cancer cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Feb 3;81(1):73. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-05107-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38308713 Free PMC article.
-
CTBP2 contributes to cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma by inhibiting generation of reactive oxygen species.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 30;13(4):1695-1706. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-2135. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38737699 Free PMC article.
-
FGFR families: biological functions and therapeutic interventions in tumors.MedComm (2020). 2023 Sep 23;4(5):e367. doi: 10.1002/mco2.367. eCollection 2023 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37750089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shake It Up Baby Now: The Changing Focus on TWIST1 and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer and Other Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 16;24(24):17539. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417539. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139368 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maron S.B., Alpert L., Kwak H.A., Lomnicki S., Chase L., Xu D., O’Day E., Nagy R.J., Lanman R.B., Cecchi F., et al. Targeted Therapies for Targeted Populations: Anti-EGFR Treatment for EGFR-Amplified Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:696–713. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-1260. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Janjigian Y.Y., Smit E.F., Groen H.J., Horn L., Gettinger S., Camidge D.R., Riely G.J., Wang B., Fu Y., Chand V.K., et al. Dual inhibition of EGFR with afatinib and cetuximab in kinase inhibitor-resistant EGFR-mutant lung cancer with and without T790M mutations. Cancer Discov. 2014;4:1036–1045. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0326. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

