Apigenin Modulates AnxA6- and TNAP-Mediated Osteoblast Mineralization
- PMID: 36361965
- PMCID: PMC9658728
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232113179
Apigenin Modulates AnxA6- and TNAP-Mediated Osteoblast Mineralization
Abstract
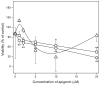
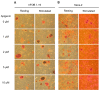
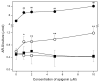
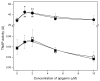
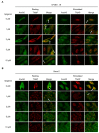
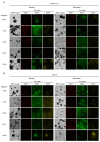
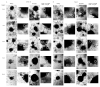
Mineralization-competent cells like osteoblasts and chondrocytes release matrix vesicles (MVs) which accumulate Ca2+ and Pi, creating an optimal environment for apatite formation. The mineralization process requires the involvement of proteins, such as annexins (Anx) and tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP), as well as low molecular-weight compounds. Apigenin, a flavonoid compound, has been reported to affect bone metabolism, but there are doubts about its mechanism of action under physiological and pathological conditions. In this report, apigenin potency to modulate annexin A6 (AnxA6)- and TNAP-mediated osteoblast mineralization was explored using three cell lines: human fetal osteoblastic hFOB 1.19, human osteosarcoma Saos-2, and human coronary artery smooth muscle cells HCASMC. We compared the mineralization competence, the morphology and composition of minerals, and the protein distribution in control and apigenin-treated cells and vesicles. The mineralization ability was monitored by AR-S/CPC analysis, and TNAP activity was determined by ELISA assay. Apigenin affected the mineral structure and modulated TNAP activity depending on the concentration. We also observed increased mineralization in Saos-2 cells. Based on TEM-EDX, we found that apigenin influenced the mineral composition. This flavonoid also disturbed the intracellular distribution of AnxA6 and TNAP, especially blocking AnxA6 aggregation and TNAP attachment to the membrane, as examined by FM analysis of cells and TEM-gold analysis of vesicles. In summary, apigenin modulates the mineralization process by regulating AnxA6 and TNAP, as well as through various effects on normal and cancer bone tissues or atherosclerotic soft tissue.
Keywords: AnxA6; TNAP; apigenin; atherosclerosis; matrix vesicles; mineralization; osteoblast; osteosarcoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Annexins A2, A6 and Fetuin-A Affect the Process of Mineralization in Vesicles Derived from Human Osteoblastic hFOB 1.19 and Osteosarcoma Saos-2 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 13;22(8):3993. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083993. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33924370 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of minerals in vesicles produced by human osteoblasts hFOB 1.19 and osteosarcoma Saos-2 cells stimulated for mineralization.J Inorg Biochem. 2017 Jun;171:100-107. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2017.03.006. Epub 2017 Mar 29. J Inorg Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28380345
-
Src and ROCK Kinases Differentially Regulate Mineralization of Human Osteosarcoma Saos-2 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 12;20(12):2872. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122872. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31212828 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of mineralization and the role of alkaline phosphatase in health and disease.J Nippon Med Sch. 2010 Feb;77(1):4-12. doi: 10.1272/jnms.77.4. J Nippon Med Sch. 2010. PMID: 20154452 Review.
-
The role of phosphatases in the initiation of skeletal mineralization.Calcif Tissue Int. 2013 Oct;93(4):299-306. doi: 10.1007/s00223-012-9672-8. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013. PMID: 23183786 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Apigenin Inhibits the Progression of Osteoarthritis by Mediating Macrophage Polarization.Molecules. 2023 Mar 24;28(7):2915. doi: 10.3390/molecules28072915. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049677 Free PMC article.
-
HuR-positive stress granules: Potential targets for age-related osteoporosis.Aging Cell. 2024 Mar;23(3):e14053. doi: 10.1111/acel.14053. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38375951 Free PMC article.
-
AnnexinA6: a potential therapeutic target gene for extracellular matrix mineralization.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Sep 4;11:1201200. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1201200. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37727505 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

