Differential Effects of Human Tau Isoforms to Neuronal Dysfunction and Toxicity in the Drosophila CNS
- PMID: 36361774
- PMCID: PMC9655709
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232112985
Differential Effects of Human Tau Isoforms to Neuronal Dysfunction and Toxicity in the Drosophila CNS
Abstract
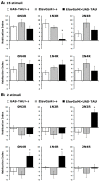
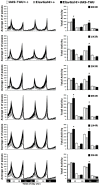
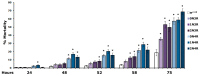
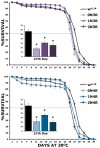
Accumulation of highly post-translationally modified tau proteins is a hallmark of neurodegenerative disorders known as tauopathies, the most common of which is Alzheimer's disease. Although six tau isoforms are found in the human brain, the majority of animal and cellular tauopathy models utilize a representative single isoform. However, the six human tau isoforms present overlapping but distinct distributions in the brain and are differentially involved in particular tauopathies. These observations support the notion that tau isoforms possess distinct functional properties important for both physiology and pathology. To address this hypothesis, the six human brain tau isoforms were expressed singly in the Drosophila brain and their effects in an established battery of assays measuring neuronal dysfunction, vulnerability to oxidative stress and life span were systematically assessed comparatively. The results reveal isoform-specific effects clearly not attributed to differences in expression levels but correlated with the number of microtubule-binding repeats and the accumulation of a particular isoform in support of the functional differentiation of these tau isoforms. Delineation of isoform-specific effects is essential to understand the apparent differential involvement of each tau isoform in tauopathies and their contribution to neuronal dysfunction and toxicity.
Keywords: Drosophila; habituation; learning and memory; neuronal dysfunction; tau isoforms; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The six brain-specific TAU isoforms and their role in Alzheimer's disease and related neurodegenerative dementia syndromes.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 May;20(5):3606-3628. doi: 10.1002/alz.13784. Epub 2024 Mar 31. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 38556838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct phenotypes of three-repeat and four-repeat human tau in a transgenic model of tauopathy.Neurobiol Dis. 2017 Sep;105:74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.05.003. Epub 2017 May 11. Neurobiol Dis. 2017. PMID: 28502805
-
Important neuronal toxicity of microtubule-bound Tau in vivo in Drosophila.Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Oct 1;20(19):3738-45. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr290. Epub 2011 Jun 24. Hum Mol Genet. 2011. PMID: 21705366
-
Transmission of tauopathy strains is independent of their isoform composition.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 7;11(1):7. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13787-x. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 31911587 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation differentiates tau-dependent neuronal toxicity and dysfunction.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Aug;38(4):981-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0380981. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20658989 Review.
Cited by
-
Choline Metabolites Reverse Differentially the Habituation Deficit and Elevated Memory of Tau Null Drosophila.Cells. 2024 Apr 25;13(9):746. doi: 10.3390/cells13090746. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38727282 Free PMC article.
-
The six brain-specific TAU isoforms and their role in Alzheimer's disease and related neurodegenerative dementia syndromes.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 May;20(5):3606-3628. doi: 10.1002/alz.13784. Epub 2024 Mar 31. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 38556838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of the Tau Protein on D. melanogaster Lifespan Depends on GSK3 Expression and Sex.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 21;24(3):2166. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032166. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768490 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sotiropoulos I., Galas M.C., Silva J.M., Skoulakis E., Wegmann S., Maina M.B., Blum D., Sayas C.L., Mandelkow E.M., Mandelkow E., et al. Atypical, non-standard functions of the microtubule associated Tau protein. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2017;5:91. doi: 10.1186/s40478-017-0489-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

