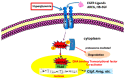
The Role of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 36359813
- PMCID: PMC9656309
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11213416
The Role of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Abstract
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is expressed in numerous cell types in the adult mammalian kidney and is activated by a family of EGF-like ligands. EGFR activation has been implicated in a variety of physiologic and pathophysiologic functions. There is increasing evidence that aberrant EGFR activation is a mediator of progressive kidney injury in diabetic kidney disease. This review will highlight recent studies indicating its potential role and mechanisms of injury of both glomerular and tubular cells in development and progression of diabetic kidney disease.
Keywords: EGF; diabetes; kidney; nephropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in acute and chronic kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2013 May;83(5):804-10. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.435. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Kidney Int. 2013. PMID: 23325080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low nitric oxide bioavailability upregulates renal heparin binding EGF-like growth factor expression.Kidney Int. 2013 Dec;84(6):1176-88. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.214. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Kidney Int. 2013. PMID: 23760291 Free PMC article.
-
Selective activation of epidermal growth factor receptor in renal proximal tubule induces tubulointerstitial fibrosis.FASEB J. 2017 Oct;31(10):4407-4421. doi: 10.1096/fj.201601359RR. Epub 2017 Jun 16. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28626027 Free PMC article.
-
Podocyte EGFR Inhibits Autophagy Through Upregulation of Rubicon in Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy.Diabetes. 2021 Feb;70(2):562-576. doi: 10.2337/db20-0660. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 33239448 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Its Ligands in Kidney Inflammation and Damage.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Dec 23;2018:8739473. doi: 10.1155/2018/8739473. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 30670929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Senescence-Associated Biomarkers in Diabetic Glomerulopathy Using Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis.J Diabetes Res. 2024 Jan 23;2024:5560922. doi: 10.1155/2024/5560922. eCollection 2024. J Diabetes Res. 2024. PMID: 38292407 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key immune-related genes and potential therapeutic drugs in diabetic nephropathy based on machine learning algorithms.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Aug 26;17(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-01995-4. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39187837 Free PMC article.
-
Network medicine based approach for identifying the type 2 diabetes, osteoarthritis and triple negative breast cancer interactome: Finding the hub of hub genes.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 22;10(17):e36650. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36650. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281650 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous