Role of CAR T Cell Metabolism for Therapeutic Efficacy
- PMID: 36358860
- PMCID: PMC9658570
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14215442
Role of CAR T Cell Metabolism for Therapeutic Efficacy
Abstract
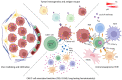
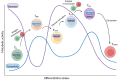
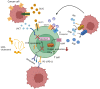
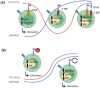
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells hold enormous potential. However, a substantial proportion of patients receiving CAR T cells will not reach long-term full remission. One of the causes lies in their premature exhaustion, which also includes a metabolic anergy of adoptively transferred CAR T cells. T cell phenotypes that have been shown to be particularly well suited for CAR T cell therapy display certain metabolic characteristics; whereas T-stem cell memory (TSCM) cells, characterized by self-renewal and persistence, preferentially meet their energetic demands through oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), effector T cells (TEFF) rely on glycolysis to support their cytotoxic function. Various parameters of CAR T cell design and manufacture co-determine the metabolic profile of the final cell product. A co-stimulatory 4-1BB domain promotes OXPHOS and formation of central memory T cells (TCM), while T cells expressing CARs with CD28 domains predominantly utilize aerobic glycolysis and differentiate into effector memory T cells (TEM). Therefore, modification of CAR co-stimulation represents one of the many strategies currently being investigated for improving CAR T cells' metabolic fitness and survivability within a hostile tumor microenvironment (TME). In this review, we will focus on the role of CAR T cell metabolism in therapeutic efficacy together with potential targets of intervention.
Keywords: CAR T cells; bioenergetics; immune escape; immunometabolism; metabolism; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
4-1BB and optimized CD28 co-stimulation enhances function of human mono-specific and bi-specific third-generation CAR T cells.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Oct;9(10):e003354. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003354. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34706886 Free PMC article.
-
CAR-T Cells with Phytohemagglutinin (PHA) Provide Anti-Cancer Capacity with Better Proliferation, Rejuvenated Effector Memory, and Reduced Exhausted T Cell Frequencies.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;11(2):313. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020313. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851194 Free PMC article.
-
Tinkering under the Hood: Metabolic Optimisation of CAR-T Cell Therapy.Antibodies (Basel). 2021 Apr 26;10(2):17. doi: 10.3390/antib10020017. Antibodies (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33925949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct Signaling of Coreceptors Regulates Specific Metabolism Pathways and Impacts Memory Development in CAR T Cells.Immunity. 2016 Feb 16;44(2):380-90. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.01.021. Immunity. 2016. PMID: 26885860
-
Importance of T, NK, CAR T and CAR NK Cell Metabolic Fitness for Effective Anti-Cancer Therapy: A Continuous Learning Process Allowing the Optimization of T, NK and CAR-Based Anti-Cancer Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 30;14(1):183. doi: 10.3390/cancers14010183. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35008348 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunotherapy for colorectal cancer.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 21;15:1433315. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1433315. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39238638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginsenoside Rg1 improves anti-tumor efficacy of adoptive cell therapy by enhancing T cell effector functions.Blood Sci. 2023 Jun 30;5(3):170-179. doi: 10.1097/BS9.0000000000000165. eCollection 2023 Jul. Blood Sci. 2023. PMID: 37546705 Free PMC article.
-
Deleting the mitochondrial respiration negative regulator MCJ enhances the efficacy of CD8+ T cell adoptive therapies in pre-clinical studies.Nat Commun. 2024 May 24;15(1):4444. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48653-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38789421 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of CAR T cell metabolism in an optimized protocol.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jun 20;11:1207576. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1207576. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37409169 Free PMC article.
-
Survival advantage of native and engineered T cells is acquired by mitochondrial transfer from mesenchymal stem cells.J Transl Med. 2024 Sep 27;22(1):868. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05627-4. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39334383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neelapu S.S., Locke F.L., Bartlett N.L., Lekakis L.J., Miklos D.B., Jacobson C.A., Braunschweig I., Oluwole O.O., Siddiqi T., Lin Y., et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017;377:2531–2544. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1707447. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

