Quercetin Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cell Damage and Inflammation via Regulation of the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway in Bovine Intestinal Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 36354668
- PMCID: PMC9688721
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb44110356
Quercetin Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cell Damage and Inflammation via Regulation of the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway in Bovine Intestinal Epithelial Cells
Abstract
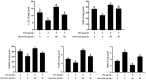
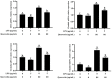
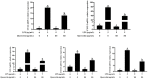
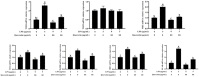
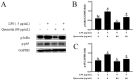
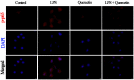
Acute diarrhoea and intestinal inflammation represent one of the most prevalent clinical disorders of milk production, resulting in enormous annual financial damage for the dairy sector. In the context of an unsatisfactory therapeutic effect of antibiotics, the natural products of plants have been the focus of research. Quercetin is an important flavonoid found in a variety of plants, including fruits and vegetables, and has strong anti-inflammatory effects, so it has received extensive attention as a potential anti-inflammatory antioxidant. However, the underlying basis of quercetin on inflammatory reactions and oxidative tension generated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in bovine intestinal epithelial cells (BIECs) is currently unexplained. This research aimed to determine the influence of quercetin on LPS-induced inflammatory reactions, oxidative tension, and the barrier role of BIECs. Our findings demonstrated that BIEC viability was significantly improved in LPS-treated BIEC with 80 μg/mL quercetin compared with the control group. Indicators of oxidative overload and genes involved in barrier role revealed that 80 μg/mL quercetin efficiently rescued BIECs from oxidative and barrier impairment triggered by 5 μg/mL LPS. In addition, the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, as well as chemokines CXCL2, CXCL5, CCL5, and CXCL8, was diminished in LPS-treated BIECs with 80 μg/mL quercetin compared with LPS alone. Furthermore, the mRNA expression of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), CD14, myeloid differential protein-2 (MD2), and myeloid differentiation primary response protein (MyD88) genes associated with the TLR4 signal mechanism was markedly reduced by the addition of quercetin to LPS-modulated BIECs, indicating that quercetin can suppress the TLR4 signal mechanism. We performed Western blotting on the NF-κB signalling mechanism and compared it with immunofluorescence to further corroborate this conclusion. The LPS treatment enhanced the proportions of p-IκBα/GAPDH and p-p65/GAPDH. Compared with the LPS-treated group, quercetin administration decreased the proportions of p-IκBα/GAPDH and p-p65/GAPDH. In addition, immunofluorescence demonstrated that quercetin greatly reduced the LPS-induced nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 in BIECs. The benefits of quercetin on inflammatory reactions in LPS-induced BIECs may be a result of its capacity to inhibit the TLR4-mediated NF-κB signalling mechanism. These findings suggest that quercetin can be used as an anti-inflammatory reagent to treat intestinal inflammation induced by LPS release.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; antioxidant; barrier function; fruit and vegetable extracts; quercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
Regarding the manuscript’s topic, we can confirm that there are no possible conflicts of interest with any financial companies.
Figures

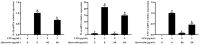
Similar articles
-
Quercetin Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells by Suppressing TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Jul 4;9:915726. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.915726. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35865878 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cell Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Responses via Regulation of the TLR4-NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Bovine Rumen Epithelial Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Aug 21;15(8):512. doi: 10.3390/toxins15080512. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37624269 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Inhibits Inflammatory Response Induced by LPS from Porphyromonas gingivalis in Human Gingival Fibroblasts via Suppressing NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Aug 20;2019:6282635. doi: 10.1155/2019/6282635. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31531360 Free PMC article.
-
Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin attenuate microglia inflammatory response via TLR4/NF-kB pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Jul 18;16(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1538-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31319868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin improves pancreatic cancer chemo-sensitivity by regulating oxidative-inflammatory networks.J Food Biochem. 2022 Dec;46(12):e14453. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14453. Epub 2022 Oct 1. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36181395 Review.
Cited by
-
The protective activity of natural flavonoids against osteoarthritis by targeting NF-κB signaling pathway.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 14;14:1117489. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1117489. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36998478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Potential Adhesin/Invasin STM0306 Participates in Host Cell Inflammation Induced by Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 3;24(9):8170. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098170. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175877 Free PMC article.
-
Discovering the Protective Effects of Quercetin on Aflatoxin B1-Induced Toxicity in Bovine Foetal Hepatocyte-Derived Cells (BFH12).Toxins (Basel). 2023 Sep 6;15(9):555. doi: 10.3390/toxins15090555. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37755981 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Protects Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity via the PI3K/Akt/Erk Signaling Pathway in a Mouse Model of Meningitis Induced by Glaesserella parasuis.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 14;14(6):696. doi: 10.3390/biom14060696. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38927100 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the potential bioactive components and mechanism of Qianhua Gout Capsules in the treatment of gouty arthritis through network pharmacology, molecular docking and pharmacodynamic study strategies.Heliyon. 2024 May 10;10(10):e30983. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30983. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38770346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takanashi N., Tomosada Y., Villena J., Murata K., Takahashi T., Chiba E., Tohno M., Shimazu T., Aso H., Suda Y., et al. Advanced application of bovine intestinal epithelial cell line for evaluating regulatory effect of lactobacilli against heat-killed enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-mediated inflammation. BMC Microbiol. 2013;13:54. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-54. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schneider M., Zimmermann A.G., Roberts R.A., Zhang L., Swanson K.V., Wen H.T., Davis B.K., Allen I.C., Holl E.K., Ye Z.M., et al. The innate immune sensor NLRC3 attenuates Toll-like receptor signaling via modification of the signaling adaptor TRAF6 and transcription factor NF-kappa B. Nat. Immunol. 2012;13:823–831. doi: 10.1038/ni.2378. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

