Preliminary Study on Natural Killer Cell Activity for Interferon-Gamma Production after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Tumors
- PMID: 36344478
- PMCID: PMC9666231
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2020.0339
Preliminary Study on Natural Killer Cell Activity for Interferon-Gamma Production after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Tumors
Abstract
Objective: High-dose radiation is well known to induce and modulate the immune system. This study was performed to evaluate the correlation between clinical outcomes and changes in natural killer cell activity (NKA) after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (GKS) in patients with brain cancer.
Methods: We performed an open-label, prospective, cross-sectional study of 38 patients who were treated with GKS for brain tumors, including metastatic and benign brain tumors. All of the patients underwent GKS, and blood samples were collected before and after GKS. NKA was measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit, to measure interferon-gamma (IFNγ) secreted by ex vivo-stimulated NK cells from whole blood. We explored the correlations between NK cell-produced IFNγ (NKA-IFNγ) levels and clinical parameters of patients who were treated with GKS for brain tumors.
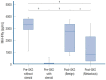
Results: NKA-IFNγ levels were decreased in metastatic brain tumor patients compared to those with benign brain tumors (p<0.0001). All the patients who used steroid treatment to reduce brain swelling after GKS had an NKA-IFNγ level of zero except one patient. High NKA-IFNγ levels were not associated with a rapid decrease in brain metastasis and did not increase after GKS.
Conclusion: The activity of NK cells in metastatic brain tumors decreased more than that in benign brain tumors after GKS.
Keywords: Gamma Knife Radiosurgery; Interferon-gamma; Natural killer cell.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and pathological analysis of benign brain tumors resected after Gamma Knife surgery.J Neurosurg. 2014 Dec;121 Suppl:179-87. doi: 10.3171/2014.8.GKS141439. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 25434951
-
Gamma knife surgery for metastatic brain tumors from renal cell carcinoma.J Neurosurg. 2006 Oct;105(4):555-60. doi: 10.3171/jns.2006.105.4.555. J Neurosurg. 2006. PMID: 17044558
-
Large intracranial metastatic tumors treated by Gamma Knife surgery: outcomes and prognostic factors.J Neurosurg. 2014 Jan;120(1):52-9. doi: 10.3171/2013.9.JNS131163. Epub 2013 Oct 25. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 24160478
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with glomus jugulare tumors.Neurosurg Focus. 2004 Aug 15;17(2):E10. doi: 10.3171/foc.2004.17.2.10. Neurosurg Focus. 2004. PMID: 15329025 Review.
-
Long-term tumor control and cranial nerve outcomes following γ knife surgery for larger-volume vestibular schwannomas.J Neurosurg. 2012 Mar;116(3):598-604. doi: 10.3171/2011.11.JNS11811. Epub 2011 Dec 16. J Neurosurg. 2012. PMID: 22175724 Review.
References
-
- Barkin J, Rodriguez-Suarez R, Betito K. Association between natural killer cell activity and prostate cancer: a pilot study. Can J Uro. 2017;24:8708–8713. - PubMed
-
- Berghoff AS, Preusser M. The inflammatory microenvironment in brain metastases: potential treatment target? Chin Clin Oncol. 2015;4:21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources