Potential predictive and therapeutic applications of small extracellular vesicles-derived circPARD3B in osteoarthritis
- PMID: 36339585
- PMCID: PMC9627215
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.968776
Potential predictive and therapeutic applications of small extracellular vesicles-derived circPARD3B in osteoarthritis
Abstract
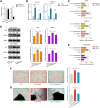
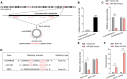
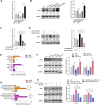
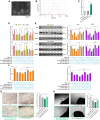
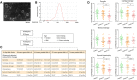
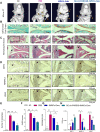
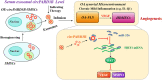
Background: Heterogeneous phenotypes that display distinct common characteristics of osteoarthritis (OA) are not well defined and will be helpful in identifying more customized therapeutic options for OA. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have attracted more and more attention due to their role in the progression of OA. Investigating the role of circRNAs in the pathogenesis of OA will contribute to the phenotyping of OA and to individualized treatment. Methods: Small extracellular vesicles (sEV) were isolated from serum samples from patients with OA of different stages and sEV-derived circPARD3B was determined using RT-qPCR analysis. CircPARD3B expression in a stimulated coculture that included OA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (OA-FLS) as well as human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMECs), plus the effects of circPARD3B on the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) long with angiogenic activity, were evaluated in vitro. Based on bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter assay (LRA), MiR-326 and sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) were found to be interactive partners of circPARD3B. Mesenchymal stem cells (SMSCs) overexpressing circPARD3B were constructed and SMSCs-derived sEV with overexpressed circPARD3B (OE-circPARD3B-SMSCs-sEV) were obtained to explore the effect of the intervention of circPARD3B combined with SMSCs-sEV-based therapy in vitro and in a OA model induced by collagenase in vivo. Results: Serum sEV-linked circPARD3B was indentified to be significantly decreased in the inflammatory phenotype of OA. Overexpression of circPARD3B was found to inhibit the expression of VEGF, as well as the angiogenesis induced by VEGF in a IL-1β stimulated the co-culture of OA-FLS as well as HDMECs. CircPARD3B is directly bound to miR-326. SIRT1 was considered a novel miR-326 target gene. OE-circPARD3B-SMSCs-sEV significantly reduced VEGF expression in coculture of OA-FLS and HDMECs. Injection of OE-circPARD3B-SMSCs-sEV could also reduce synovial VEGF; additionally, it could further ameliorate OA in the mouse model of OA in vivo. Conclusion: Serum sEV circPARD3B is a potential biomarker that enables the identification of the inflammatory phenotype of patients with OA. Correspondingly, intracellular transfer of circPARD3B through OE-circPARD3B-SMSCs-sEV could postpone disease progression through a functional module regulated angiogenesis of circPARD3B-miR-326-SIRT1, providing a novel therapeutic strategy for OA.
Keywords: SIRT1; VEGF; circPARD3B; osteoarthritis; small extracellular vesicles (sEV).
Copyright © 2022 Lin, Ma, Zhu, Dai, Sun, Li, Niu, Chu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SMSCs-derived sEV overexpressing miR-433-3p inhibits angiogenesis induced by sEV released from synoviocytes under triggering of ferroptosis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Mar;116:109875. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109875. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37501360
-
Therapeutic Potential of Exosomal circRNA Derived from Synovial Mesenchymal Cells via Targeting circEDIL3/miR-485-3p/PIAS3/STAT3/VEGF Functional Module in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Dec 3;16:7977-7994. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S333465. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34887661 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial mesenchymal stem cells effectively alleviate osteoarthritis through promoting the proliferation and differentiation of meniscus chondrocytes.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Feb;24(4):1645-1655. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202002_20338. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32141530
-
Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles containing microRN555A-26a-5p ameliorate cartilage damage of osteoarthritis.J Gene Med. 2021 Nov;23(11):e3379. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3379. Epub 2021 Aug 11. J Gene Med. 2021. PMID: 34296780
-
Small extracellular vesicles in combination with sleep-related circRNA3503: A targeted therapeutic agent with injectable thermosensitive hydrogel to prevent osteoarthritis.Bioact Mater. 2021 May 6;6(12):4455-4469. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.04.031. eCollection 2021 Dec. Bioact Mater. 2021. PMID: 34027234 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulatory mechanism of circular RNA involvement in osteoarthritis.Front Surg. 2023 Jan 6;9:1049513. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1049513. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 36684373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Classical Intercellular Communications: Basic Mechanisms and Roles in Biology and Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 29;24(7):6455. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076455. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutics of the future: Navigating the pitfalls of extracellular vesicles research from an osteoarthritis perspective.J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Jul;13(7):e12435. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12435. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024. PMID: 38943211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding RNAs in skeletal development and disorders.Biol Res. 2024 Apr 22;57(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00497-y. Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 38644509 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altman R., Asch E., Bloch D., Bole G., Borenstein D., Brandt K., et al. (1986). Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum. 29, 1039–1049. 10.1002/art.1780290816 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alvaro-Gracia J. M., Zvaifler N. J., Firestein G. S. (1990). Cytokines in chronic inflammatory arthritis. V. Mutual antagonism between interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on HLA-DR expression, proliferation, collagenase production, and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production by rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. J. Clin. Invest. 86, 1790–1798. 10.1172/JCI114908 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

