Moroccan Medicinal Plants Used to Treat Cancer: Ethnomedicinal Study and Insights into Pharmacological Evidence
- PMID: 36330227
- PMCID: PMC9626195
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1645265
Moroccan Medicinal Plants Used to Treat Cancer: Ethnomedicinal Study and Insights into Pharmacological Evidence
Abstract
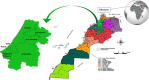
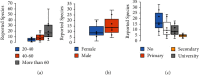
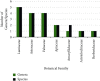
Cancer is one of the major medical challenges, with an unacceptably high death toll worldwide. In Morocco, medicinal plants continue to play a pivotal therapeutic role despite the development of modern sanitation systems. In the current study, an ethnobotanical survey was carried out at the Moroccan national institute of oncology, Rabat, and we aimed at (1) establishing an exhaustive inventory of indigenous knowledge of Moroccan medicinal plants used to manage cancer and (2) confirming the reported ethnopharmacological uses through bibliometric review. An ethnobotanical survey was conducted with 291 cancer patients at the Moroccan National Institute of Oncology, Rabat, during a period of 4 months, from February to May 2019, through semistructured interviews. Ethnobotanical indices, including informant consensus factor (FIC), use report (UR), relative frequency citation (RFC), botanical family use value (FUV), fidelity level (FL), and index of agreement on remedies (IAR), were employed in data analyses. The survey revealed that 39 medicinal plants belonging to 27 botanical families and 38 genera were used to treat cancer. The most used ethnospecies were Aristolochia longa with the highest RFC value (0.096), followed by Nigella sativa, Ephedra alata, Euphorbia resinifera, and Lavandula dentata, éwith RFC values of 0.072, 0.054, 0.044, and 0.044, respectively. In regard to the plant families, Lamiaceae contributed the highest number of plants with five species (FUV = 0.034), followed by Asteraceae (4 species; FUV = 0.020), and Fabaceae (4 species; FUV = 0.020). The leaves are the most popular plant part used by the studied population against cancer; otherwise, decoction was the most commonly used method for remedy preparation and the highest FIC was noticed for uterine cancer treatment (0.86). Considering these findings, further investigations into the recorded plant species should be performed to assess phytochemical constituents and pharmaceutical benefits in order to identify their active compounds for any drug formulations.
Copyright © 2022 Naoufal El Hachlafi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ethnomedicinal application of native remedies used against diabetes and related complications in Mauritius.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;151(1):413-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.10.069. Epub 2013 Nov 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24231070
-
Ethnobotanical Study Aimed at Investigating the Use of Medicinal Plants to Treat Nervous System Diseases in the Rif of Morocco.J Chiropr Med. 2020 Mar;19(1):70-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jcm.2020.02.004. Epub 2020 Sep 1. J Chiropr Med. 2020. PMID: 33192194 Free PMC article.
-
Wild medicinal and food plants used by communities living in Mopane woodlands of southern Angola: Results of an ethnobotanical field investigation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jan 11;177:126-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.11.041. Epub 2015 Nov 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26639153
-
Anticancer medicinal plants used by Moroccan people: Ethnobotanical, preclinical, phytochemical and clinical evidence.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Feb 10;266:113435. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113435. Epub 2020 Oct 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33022340 Review.
-
Moroccan medicinal plants traditionally used for the treatment of skin diseases: From ethnobotany to clinical trials.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Oct 28;297:115532. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115532. Epub 2022 Jul 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35843409 Review.
Cited by
-
Current and potential future biological uses of Saussurea costus (Falc.) Lipsch: A comprehensive review.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 11;10(18):e37790. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37790. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39323795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant, Volatile Compounds; Antimicrobial, Anti-Inflammatory, and Dermatoprotective Properties of Cedrus atlantica (Endl.) Manetti Ex Carriere Essential Oil: In Vitro and In Silico Investigations.Molecules. 2023 Aug 6;28(15):5913. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155913. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37570883 Free PMC article.
-
Ethnobotanical survey and scientific validation of liver-healing plants in northeastern Morocco.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 10;15:1414190. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1414190. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39318777 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal plants used in the management of cancers by residents in the Elgon Sub-Region, Uganda.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Dec 12;23(1):450. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04273-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 38087230 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Chemically-Characterized Essential Oils from Eucalyptus polybractea, Ormenis mixta, and Lavandula burnatii: Optimization of a New Complete Antibacterial Formulation Using Simplex-Centroid Mixture Design.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2023 Aug 21;2023:5593350. doi: 10.1155/2023/5593350. eCollection 2023. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 37645561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohamed A., Karima S., Nadia O. The use of medicinal plants against cancer: an ethnobotanical study in the Beni mellal-khenifra region in Morocco. European Journal of Integrative Medicine . 2022;52 doi: 10.1016/j.eujim.2022.102137.102137 - DOI
-
- Center M., Siegel R., Jemal A. Global cancer facts & figures. American Cancer Society . 2011;3:1–52.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

