Platelets and platelet extracellular vesicles in drug delivery therapy: A review of the current status and future prospects
- PMID: 36330089
- PMCID: PMC9623298
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1026386
Platelets and platelet extracellular vesicles in drug delivery therapy: A review of the current status and future prospects
Abstract
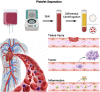
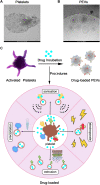
Platelets are blood cells that are primarily produced by the shedding of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow. Platelets participate in a variety of physiological and pathological processes in vivo, including hemostasis, thrombosis, immune-inflammation, tumor progression, and metastasis. Platelets have been widely used for targeted drug delivery therapies for treating various inflammatory and tumor-related diseases. Compared to other drug-loaded treatments, drug-loaded platelets have better targeting, superior biocompatibility, and lower immunogenicity. Drug-loaded platelet therapies include platelet membrane coating, platelet engineering, and biomimetic platelets. Recent studies have indicated that platelet extracellular vesicles (PEVs) may have more advantages compared with traditional drug-loaded platelets. PEVs are the most abundant vesicles in the blood and exhibit many of the functional characteristics of platelets. Notably, PEVs have excellent biological efficacy, which facilitates the therapeutic benefits of targeted drug delivery. This article provides a summary of platelet and PEVs biology and discusses their relationships with diseases. In addition, we describe the preparation, drug-loaded methods, and specific advantages of platelets and PEVs targeted drug delivery therapies for treating inflammation and tumors. We summarize the hot spots analysis of scientific articles on PEVs and provide a research trend, which aims to give a unique insight into the development of PEVs research focus.
Keywords: drug-loaded; inflammation; platelet extracellular vesicles; platelets; targeted drug delivery; tumors.
Copyright © 2022 Dai, Zhao, Song, Pan, Yang, Zhu, Chen, Zhang and Xia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Beyond Blood Clotting: The Many Roles of Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 14;12(8):1850. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081850. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet extracellular vesicles are efficient delivery vehicles of doxorubicin, an anti-cancer drug: preparation and in vitro characterization.Platelets. 2023 Dec;34(1):2237134. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2023.2237134. Platelets. 2023. PMID: 37580876
-
Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles for drug delivery.Biomater Sci. 2023 Aug 22;11(17):5758-5768. doi: 10.1039/d3bm00893b. Biomater Sci. 2023. PMID: 37489841 Review.
-
The potential utilization of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles in clinical treatment.Platelets. 2024 Dec;35(1):2397592. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2024.2397592. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Platelets. 2024. PMID: 39287127 Review.
-
Platelet-derived- Extracellular Vesicles Promote Hemostasis and Prevent the Development of Hemorrhagic Shock.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 27;9(1):17676. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53724-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31776369 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bleeding and Thrombosis in Multiple Myeloma: Platelets as Key Players during Cell Interactions and Potential Use as Drug Delivery Systems.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 1;24(21):15855. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115855. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-derived microparticles and their cargos: The past, present and future.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2024 Apr;19(2):100907. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2024.100907. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 38623487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelets, Protean Cells with All-Around Functions and Multifaceted Pharmacological Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 26;24(5):4565. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054565. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Platelet Rich Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Regenerative Medicine: A Systematic-Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 22;24(17):13043. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713043. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37685849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond Blood Clotting: The Many Roles of Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 14;12(8):1850. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081850. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200314 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alcayaga-Miranda F., Gonzalez P. L., Lopez-Verrilli A., Varas-Godoy M., Aguila-Diaz C., Contreras L., et al. (2016). Prostate tumor-induced angiogenesis is blocked by exosomes derived from menstrual stem cells through the inhibition of reactive oxygen species. Oncotarget 7 (28), 44462–44477. 10.18632/oncotarget.9852 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

