Single-Cell Microgels for Diagnostics and Therapeutics
- PMID: 36329867
- PMCID: PMC9629779
- DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202009946
Single-Cell Microgels for Diagnostics and Therapeutics
Abstract
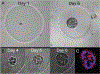
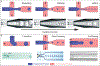
Cell encapsulation within hydrogel droplets is transforming what is feasible in multiple fields of biomedical science such as tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, in vitro modeling, and cell-based therapies. Recent advances have allowed researchers to miniaturize material encapsulation complexes down to single-cell scales, where each complex, termed a single-cell microgel, contains only one cell surrounded by a hydrogel matrix while remaining <100 μm in size. With this achievement, studies requiring single-cell resolution are now possible, similar to those done using liquid droplet encapsulation. Of particular note, applications involving long-term in vitro cultures, modular bioinks, high-throughput screenings, and formation of 3D cellular microenvironments can be tuned independently to suit the needs of individual cells and experimental goals. In this progress report, an overview of established materials and techniques used to fabricate single-cell microgels, as well as insight into potential alternatives is provided. This focused review is concluded by discussing applications that have already benefited from single-cell microgel technologies, as well as prospective applications on the cusp of achieving important new capabilities.
Keywords: 3D cell culture; cell-based therapies; hydrogels; regenerative medicine; single-cell analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
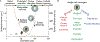

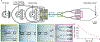


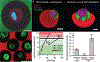
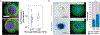

Similar articles
-
How Microgels Can Improve the Impact of Organ-on-Chip and Microfluidic Devices for 3D Culture: Compartmentalization, Single Cell Encapsulation and Control on Cell Fate.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Sep 23;13(19):3216. doi: 10.3390/polym13193216. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34641032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In-air production of 3D co-culture tumor spheroid hydrogels for expedited drug screening.Acta Biomater. 2019 Aug;94:392-409. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.06.012. Epub 2019 Jun 12. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31200118
-
Delivery of Endothelial Cell-Laden Microgel Elicits Angiogenesis in Self-Assembling Ultrashort Peptide Hydrogels In Vitro.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 Jun 30;13(25):29281-29292. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c03787. Epub 2021 Jun 18. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 34142544
-
Single-Cell Microgels: Technology, Challenges, and Applications.Trends Biotechnol. 2018 Aug;36(8):850-865. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Trends Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29656795 Review.
-
High-throughput microgel biofabrication via air-assisted co-axial jetting for cell encapsulation, 3D bioprinting, and scaffolding applications.Biofabrication. 2023 Apr 4;15(3):035001. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/acc4eb. Biofabrication. 2023. PMID: 36927673 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Microgels for Cell Delivery in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.Nanomicro Lett. 2024 Jun 17;16(1):218. doi: 10.1007/s40820-024-01421-5. Nanomicro Lett. 2024. PMID: 38884868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Microgels Can Improve the Impact of Organ-on-Chip and Microfluidic Devices for 3D Culture: Compartmentalization, Single Cell Encapsulation and Control on Cell Fate.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Sep 23;13(19):3216. doi: 10.3390/polym13193216. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34641032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microencapsulation-based cell therapies.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jun 8;79(7):351. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04369-0. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35674842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The microparticulate inks for bioprinting applications.Mater Today Bio. 2023 Dec 26;24:100930. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100930. eCollection 2024 Feb. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 38293631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modular microfluidics for life sciences.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Mar 11;21(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01846-x. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 36906553 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garcia HG, Berrocal A, Kim YJ, Martini G, Zhao J, Curr. Top. Dev. Biol 2020, 137, 1. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
