The role of macrophage scavenger receptor 1 (MSR1) in inflammatory disorders and cancer
- PMID: 36325338
- PMCID: PMC9618966
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1012002
The role of macrophage scavenger receptor 1 (MSR1) in inflammatory disorders and cancer
Abstract
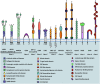
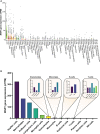
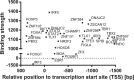
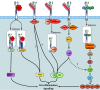
Macrophage scavenger receptor 1 (MSR1), also named CD204, holds key inflammatory roles in multiple pathophysiologic processes. Present primarily on the surface of various types of macrophage, this receptor variably affects processes such as atherosclerosis, innate and adaptive immunity, lung and liver disease, and more recently, cancer. As highlighted throughout this review, the role of MSR1 is often dichotomous, being either host protective or detrimental to the pathogenesis of disease. We will discuss the role of MSR1 in health and disease with a focus on the molecular mechanisms influencing MSR1 expression, how altered expression affects disease process and macrophage function, the limited cell signalling pathways discovered thus far, the emerging role of MSR1 in tumour associated macrophages as well as the therapeutic potential of targeting MSR1.
Keywords: CD204; MSR1; cancer; immunology; inflammation; macrophages.
Copyright © 2022 Gudgeon, Marín-Rubio and Trost.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Triggering MSR1 promotes JNK-mediated inflammation in IL-4-activated macrophages.EMBO J. 2019 Jun 3;38(11):e100299. doi: 10.15252/embj.2018100299. Epub 2019 Apr 26. EMBO J. 2019. PMID: 31028084 Free PMC article.
-
RNA helicase DDX5 participates in oxLDL-induced macrophage scavenger receptor 1 expression by suppressing mRNA degradation.Exp Cell Res. 2018 May 15;366(2):114-120. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.03.003. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Exp Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 29522752
-
High-Expressed Macrophage Scavenger Receptor 1 Predicts Severity Clinical Outcome in Transplant Patient in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Disease.J Immunol Res. 2021 Jan 31;2021:6690100. doi: 10.1155/2021/6690100. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33604393 Free PMC article.
-
Detailed role of SR-A1 and SR-E3 in tumor biology, progression, and therapy.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Sep;82(3):1735-1750. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01350-5. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38884861 Review.
-
Role of macrophage scavenger receptor MSR1 in the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 15;13:1050984. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1050984. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36591228 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The mechanism of low molecular weight fucoidan-incorporated nanofiber scaffolds inhibiting oral leukoplakia via SR-A/Wnt signal axis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 22;15:1397761. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1397761. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39104391 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of ozone alleviation of malignant ascites in hepatocellular carcinoma through the inhibition of neutrophil extracellular traps.PNAS Nexus. 2023 Aug 24;2(9):pgad280. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad280. eCollection 2023 Sep. PNAS Nexus. 2023. PMID: 37693209 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the study of macrophage polarization in inflammatory immune skin diseases.J Inflamm (Lond). 2023 Oct 12;20(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12950-023-00360-z. J Inflamm (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37828492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a distinct cluster of GDF15high macrophages induced by in vitro differentiation exhibiting anti-inflammatory activities.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 8;15:1309739. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1309739. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38655264 Free PMC article.
-
Scavenger receptor A-mediated nanoparticles target M1 macrophages for acute liver injury.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023 May;18(3):100813. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2023.100813. Epub 2023 May 9. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 37274920 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

