Differentially Expressed mRNAs and Potential Mechanisms of Radiation-Induced TUT4-/- Esophageal Cell Injury
- PMID: 36324561
- PMCID: PMC9620258
- DOI: 10.1177/15593258221136810
Differentially Expressed mRNAs and Potential Mechanisms of Radiation-Induced TUT4-/- Esophageal Cell Injury
Abstract
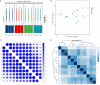
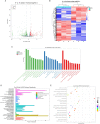
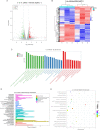
Radiation-induced esophageal injury remains a limitation for the process of radiotherapy for lung and esophageal cancer patients. Esophageal epithelial cells are extremely sensitive to irradiation, nevertheless, factors involved in the radiosensitivity of esophageal epithelial cells are still unknown. Terminal uridyl transferase 4 (TUT4) could modify the sequence of miRNAs, which affect their regulation on miRNA targets and function. In this study, we used transcriptome sequencing technology to identify mRNAs that were differentially expressed before and after radiotherapy in esophageal epithelial cells. We further explored the mRNA expression profiles between wild-type and TUT4 knockout esophageal epithelial cells. Volcano and heatmap plots unsupervised hierarchical clustering analysis were performed to classify the samples. Enrichment analysis on Gene Ontology functional annotations and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways was performed. We annotated differential genes from metabolism, genetic information processing, environmental information processing, cellular processes, and organismal systems human diseases. The aberrantly expressed genes are significantly enriched in irradiation-related biological processes, such as DNA replication, ferroptosis, and cell cycle. Moreover, we explored the distribution of transcription factor family and its target genes in differential genes. These mRNAs might serve as therapeutic targets in TUT4-related radiation-induced esophageal injury.
Keywords: esophageal epithelial; radiation-induced esophageal injury; radiosensitivity; terminal uridyl transferase 4.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Construction and analysis of mRNA, miRNA, lncRNA, and TF regulatory networks reveal the key genes associated with prostate cancer.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 23;13(8):e0198055. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198055. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30138363 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks during osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.BMC Genomics. 2022 Jun 7;23(1):425. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08646-x. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35672672 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput mRNA and miRNA profiling of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in MDCK cells.BMC Genomics. 2015 Nov 16;16:944. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2036-9. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26572553 Free PMC article.
-
An RNA-seq-Based Expression Profiling of Radiation-Induced Esophageal Injury in a Rat Model.Dose Response. 2019 May 5;17(2):1559325819843373. doi: 10.1177/1559325819843373. eCollection 2019 Apr-Jun. Dose Response. 2019. PMID: 31105479 Free PMC article.
-
Landscape of expression profiles in esophageal carcinoma by The Cancer Genome Atlas data.Dis Esophagus. 2016 Nov;29(8):920-928. doi: 10.1111/dote.12416. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Dis Esophagus. 2016. PMID: 26402921
References
-
- Wang N, Jia Y, Wang J, et al. Prognostic significance of lymph node ratio in esophageal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(4):2335-2341. - PubMed
-
- Stephans KL, Djemil T, Diaconu C, et al. Esophageal dose tolerance to hypofractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy: Risk factors for late toxicity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;90(1):197-202. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Ad V, Leiby B, Witek M, et al. Treatment-related acute esophagitis for patients with locoregionally advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with involved-field radiotherapy and concurrent chemotherapy. Am J Clin Oncol. 2014;37(5):433-437. - PubMed
-
- Vujaskovic Z, Thrasher BA, Jackson IL, Brizel MB, Brizel DM. Radioprotective effects of amifostine on acute and chronic esophageal injury in rodents. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;69(2):534-540. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

