Extracellular vesicles isolated from hyperuricemia patients might aggravate airway inflammation of COPD via senescence-associated pathway
- PMID: 36324164
- PMCID: PMC9628085
- DOI: 10.1186/s12950-022-00315-w
Extracellular vesicles isolated from hyperuricemia patients might aggravate airway inflammation of COPD via senescence-associated pathway
Abstract
Backgrounds: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a major health issue resulting in significant mortality worldwide. Due to the high heterogeneity and unclear pathogenesis, the management and therapy of COPD are still challenging until now. Elevated serum uric acid(SUA) levels seem to be associated with the inflammatory level in patients with COPD. However, the underlying mechanism is not yet clearly established. In the current research, we aim to elucidate the effect of high SUA levels on airway inflammation among COPD patients.
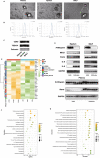
Methods: Through bioinformatic analysis, the common potential key genes were determined in both COPD and hyperuricemia (HUA) patients. A total of 68 COPD patients aged 50-75-year were included in the study, and their clinical parameters, including baseline characteristics, lung function test, as well as blood chemistry test were recorded. These parameters were then compared between the COPD patients with and without HUA. Hematoxylin & Eosin (HE), immunofluorescence (IF), and Masson trichrome staining were performed to demonstrate the pathological changes in the lung tissues. Furthermore, we isolated extracellular vesicles (EVs) from plasma, sputum, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) samples and detected the expression of inflammatory factor (Interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8 and COPD related proteases (antitrypsin and elastase) between two groups. Additionally, we treated the human bronchial epithelial (HBE) cells with cigarette smoke extract (CSE), and EVs were derived from the plasma in vitro experiments. The critical pathway involving the relationship between COPD and HUA was eventually validated based on the results of RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and western blot (WB).
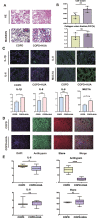
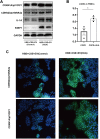
Results: In the study, the COPD patients co-existing with HUA were found to have more loss of pulmonary function compared with those COPD patients without HUA. The lung tissue samples of patients who had co-existing COPD and HUA indicated greater inflammatory cell infiltration, more severe airway destruction and even fibrosis. Furthermore, the high SUA level could exacerbate the progress of airway inflammation in COPD through the transfer of EVs. In vitro experiments, we determined that EVs isolated from plasma, sputum, and BALF played pivotal roles in the CSE-induced inflammation of HBE. The EVs in HUA patients might exacerbate both systemic inflammation and airway inflammatory response via the senescence-related pathway.
Conclusion: The pulmonary function and clinical indicators of COPD patients with HUA were worse than those without HUA, which may be caused by the increased airway inflammatory response through the EVs in the patient's peripheral blood. Moreover, it might mediate the EVs via senescence-related pathways in COPD patients with HUA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human epididymis protein 4 aggravates airway inflammation and remodeling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Respir Res. 2022 May 12;23(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02040-7. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 35550579 Free PMC article.
-
Anemoside B4 prevents chronic obstructive pulmonary disease through alleviating cigarette smoke-induced inflammatory response and airway epithelial hyperplasia.Phytomedicine. 2022 Dec;107:154431. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154431. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36115169
-
Hypoxic hUCMSC-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate allergic airway inflammation and airway remodeling in chronic asthma mice.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jan 6;12(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-02072-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33407872 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles from Airway Secretions: New Insights in Lung Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 8;22(2):583. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020583. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33430153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).J Thorac Dis. 2019 Oct;11(Suppl 17):S2141-S2154. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.10.16. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31737342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Robust positive association between serum urate and the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: hospital-based cohort and Mendelian randomisation study.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2024 Mar 13;11(1):e002203. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2023-002203. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38479817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kir E, Guven Atici A, Gullu YT, et al. The relationship between serum uric acid level and uric acid/creatinine ratio with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease severity (stable or acute exacerbation) and the development of cor pulmonale [J] Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75(8):e14303. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.14303. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

