Prime editing optimized RTT permits the correction of the c.8713C>T mutation in DMD gene
- PMID: 36320324
- PMCID: PMC9587501
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.09.022
Prime editing optimized RTT permits the correction of the c.8713C>T mutation in DMD gene
Abstract
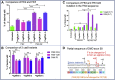
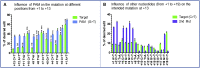
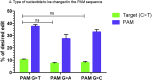
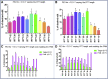
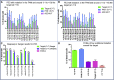
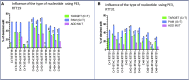
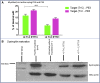
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a severe debilitating genetic disease caused by different mutations in the DMD gene leading to the absence of dystrophin protein under the sarcolemma. We used CRISPR-Cas9 prime editing technology for correction of the c.8713C>T mutation in the DMD gene and tested different variations of reverse transcription template (RTT) sequences. We increased by 3.8-fold the editing percentage of the target nucleotide located at +13. A modification of the protospacer adjacent motif sequence (located at +6) and a silent mutation (located at +9) were also simultaneously added to the target sequence modification. We observed significant differences in editing efficiency in interconversion of different nucleotides and the distance between the target, the nicking site, and the additional mutations. We achieved 22% modifications in myoblasts of a DMD patient, which led to dystrophin expression detected by western blot in the myotubes that they formed. RTT optimization permitted us to improve the prime editing of a point mutation located at +13 nucleotides from the nick site to restore dystrophin protein.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; DMD gene; Duchenne muscular dystrophy; MT: RNA/DNA editing; RTT; c.8713C>T mutation; prime editing.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prime editing strategies to mediate exon skipping in DMD gene.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 May 25;10:1128557. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1128557. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37305116 Free PMC article.
-
Prime Editing Permits the Introduction of Specific Mutations in the Gene Responsible for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 31;23(11):6160. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116160. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682838 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of In-Frame Deletion, Homology-Directed Repair, and Prime Editing-Based Correction of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Mutations.Biomolecules. 2023 May 22;13(5):870. doi: 10.3390/biom13050870. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37238739 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular correction of Duchenne muscular dystrophy by splice modulation and gene editing.RNA Biol. 2021 Jul;18(7):1048-1062. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1874161. Epub 2021 Jan 20. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33472516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Restoration of dystrophin expression and correction of Duchenne muscular dystrophy by genome editing.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2021 Aug;21(8):1049-1061. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2021.1872539. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33401973 Review.
Cited by
-
Prime editing strategies to mediate exon skipping in DMD gene.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 May 25;10:1128557. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1128557. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37305116 Free PMC article.
-
Gene editing innovations and their applications in cardiomyopathy research.Dis Model Mech. 2023 May 1;16(5):dmm050088. doi: 10.1242/dmm.050088. Epub 2023 May 24. Dis Model Mech. 2023. PMID: 37222281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytosine base editors optimized for genome editing in potato protoplasts.Front Genome Ed. 2023 Aug 30;5:1247702. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2023.1247702. eCollection 2023. Front Genome Ed. 2023. PMID: 37719877 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-Based Gene Therapies: From Preclinical to Clinical Treatments.Cells. 2024 May 8;13(10):800. doi: 10.3390/cells13100800. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38786024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prime Editing for Human Gene Therapy: Where Are We Now?Cells. 2023 Feb 7;12(4):536. doi: 10.3390/cells12040536. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36831203 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ciafaloni E., Kumar A., Liu K., Pandya S., Westfield C., Fox D.J., Caspers Conway K.M., Cunniff C., Mathews K., West N., et al. Age at onset of first signs or symptoms predicts age at loss of ambulation in Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophy: Data from the MD STARnet. J. Pediatr. Rehabil. Med. 2016;9:5–11. doi: 10.3233/PRM-160361. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

