Exploring the mechanism of andrographolide in the treatment of gastric cancer through network pharmacology and molecular docking
- PMID: 36319798
- PMCID: PMC9626486
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-18319-0
Exploring the mechanism of andrographolide in the treatment of gastric cancer through network pharmacology and molecular docking
Abstract
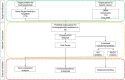
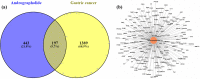
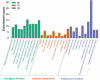
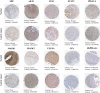
Gastric cancer has emerged as a key challenge in oncology research as a malignant tumour with advanced stage detection. Apart from surgical management, a pharmacotherapeutic approach to stomach cancer treatment is an appealing option to consider. Andrographolide has been shown to have anticancer and chemosensitizer properties in a variety of solid tumors, including stomach cancer but the exact molecular mechanism is skeptical. In this study, we identified and validated pharmacological mechanism involved in the treatment of GC with integrated approach of network pharmacology and molecular docking. The targets of andrographolide and GC were obtained from databases. The intersected targets between andrographolide and GC-related genes were used to construct protein-protein interaction (PPI) network. Furthermore, mechanism of action of the targets was predicted by Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses. Finally, these results were validated by molecular docking experiments, mRNA and protein expression level. A total of 197 targets were obtained for andrographolide treating GC. Functional enrichment analysis revealed that the target genes were exerted promising therapeutic effects on GC by HIF-1 and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. The possible mechanism of action is by inactivation of HIF-1 signaling pathway which is dependent on the inhibition of upstream PI3K-AKT pathway. The PPI network identified SRC, AKT1, TP53, STAT3, PIK3CA, MAPK1, MAPK3, VEGFA, JUN and HSP90AA1 as potential hub targets. In addition, these results were further validated with molecular docking experiments. Survival analysis indicated that the expression levels of the hub genes were significantly associated with the clinical prognosis of GC. This study provided a novel approach to reveal the therapeutic mechanisms of andrographolide on GC, making future clinical application of andrographolide in the treatment of GC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A network pharmacology approach and experimental validation to investigate the anticancer mechanism and potential active targets of ethanol extract of Wei-Tong-Xin against colorectal cancer through induction of apoptosis via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Mar 1;303:115933. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115933. Epub 2022 Nov 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36403742
-
Exploring the mechanism of Erteng-Sanjie capsule in treating gastric and colorectal cancers via network pharmacology and in-vivo validation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jun 12;327:117945. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117945. Epub 2024 Feb 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38428659
-
Exploring the mechanism of ellagic acid against gastric cancer based on bioinformatics analysis and network pharmacology.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Dec;27(23):3878-3896. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17967. Epub 2023 Oct 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37794689 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the therapeutic mechanism of Xiaotan Sanjie Formula for gastric cancer via network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Nov 17;102(46):e35986. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035986. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37986339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the Mechanisms of Bisdemethoxycurcumin in Ulcerative Colitis: Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification.Molecules. 2022 Dec 21;28(1):68. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010068. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615264 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PPARG and the PTEN-PI3K/AKT Signaling Axis May Cofunction in Promoting Chemosensitivity in Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.PPAR Res. 2024 Mar 11;2024:2271214. doi: 10.1155/2024/2271214. eCollection 2024. PPAR Res. 2024. PMID: 38505269 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Cancer Agent: The Labdane Diterpenoid-Andrographolide.Plants (Basel). 2023 May 12;12(10):1969. doi: 10.3390/plants12101969. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37653887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Andrographolide Alleviates Oxidative Damage and Inhibits Apoptosis Induced by IHNV Infection via CTSK/BCL2/Cytc Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 25;25(1):308. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010308. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. Retraction in: Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 30;26(1):208. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010208. PMID: 38203479 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Verma HK, Ratre YK, Mazzone P, Laurino S, Bhaskar LVKS. Micro RNA facilitated chemoresistance in gastric cancer: A novel biomarkers and potential therapeutics. Alexandria J. Med. 2020;56:81–92. doi: 10.1080/20905068.2020.1779992. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

