Assessing Immunogenicity of Biologic Drugs in Inflammatory Joint Diseases: Progress Towards Personalized Medicine
- PMID: 36315391
- PMCID: PMC9649489
- DOI: 10.1007/s40259-022-00559-1
Assessing Immunogenicity of Biologic Drugs in Inflammatory Joint Diseases: Progress Towards Personalized Medicine
Abstract
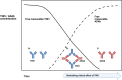
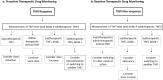
Biologic drugs have greatly improved treatment outcomes of inflammatory joint diseases, but a substantial proportion of patients either do not respond to treatment or lose response over time. Drug immunogenicity, manifested as the formation of anti-drug antibodies (ADAb), constitute a significant clinical problem. Anti-drug antibodies influence the pharmacokinetics of the drug, are associated with reduced clinical efficacy, and an increased risk of adverse events such as infusion reactions. The prevalence of ADAb differs among drugs and diseases, and the detection of ADAb also depends on the assay format. Most data exist for the tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors infliximab and adalimumab, with a frequency of ADAb that ranges from 10 to 60% across studies. Measurement of ADAb and serum drug concentrations, therapeutic drug monitoring, has been suggested as a strategy to optimize therapy with biologic drugs. Although the recent randomized clinical Norwegian Drug Monitoring (NOR-DRUM) trials show promise towards a personalized medicine prescribing approach by therapeutic drug monitoring, several challenges remain. A plethora of assay formats, with widely differing properties, is currently used for measuring ADAb. Comparing results between different assays and laboratories is difficult, which complicates the development of cut-offs necessary for guidelines and the implementation of ADAb measurements in clinical practice. With the possible exception of infliximab, limited data on clinical relevance and cost effectiveness exist to support therapeutic drug monitoring as a routine clinical strategy to monitor biologic drugs in inflammatory joint diseases. The aim of this review is to provide an overview of the characteristics and prevalence of ADAb, predisposing factors to ADAb formation, commonly used assessment methods, clinical consequences of ADAb, and the potential implications of ADAb assessments for everyday treatment of inflammatory joint diseases.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
GLG has received honoraria, consulting fees, and payment for lectures from Pfizer, AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, Orion Pharma, Sandoz, Novartis, and UCB, all unrelated to the present work. JEG, MKB, MJ, NB, and SWS report no relevant disclosures.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Risk factors for anti-drug antibody formation to infliximab: Secondary analyses of a randomised controlled trial.J Intern Med. 2022 Sep;292(3):477-491. doi: 10.1111/joim.13495. Epub 2022 Apr 26. J Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35411981 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Personalized medicine in rheumatoid arthritis: How immunogenicity impacts use of TNF inhibitors.Autoimmun Rev. 2020 May;19(5):102509. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102509. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Autoimmun Rev. 2020. PMID: 32173513
-
Anti-TROVE2 Antibody Determined by Immune-Related Array May Serve as a Predictive Marker for Adalimumab Immunogenicity and Effectiveness in RA.J Immunol Res. 2021 Mar 8;2021:6656121. doi: 10.1155/2021/6656121. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33763493 Free PMC article.
-
Antidrug antibodies (ADAb) to tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-specific neutralising agents in chronic inflammatory diseases: a real issue, a clinical perspective.Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 Feb;72(2):165-78. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202545. Epub 2012 Nov 24. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013. PMID: 23178294 Review.
-
Comparative Immunogenicity of TNF Inhibitors: Impact on Clinical Efficacy and Tolerability in the Management of Autoimmune Diseases. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.BioDrugs. 2015 Aug;29(4):241-58. doi: 10.1007/s40259-015-0134-5. BioDrugs. 2015. PMID: 26280210 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic serum level for adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis: explorative analyses of data from a randomised phase III trial.RMD Open. 2024 Nov 13;10(4):e004888. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2024-004888. RMD Open. 2024. PMID: 39537558 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase 3, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled clinical trial to compare BAT1806/BIIB800, a tocilizumab biosimilar, with tocilizumab reference product in participants with moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis with inadequate response to methotrexate: treatment period 2 analysis (week 24 to week 48).Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Sep 7;26(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03375-w. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39244595 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Proactive therapeutic drug monitoring of biologic drugs in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, inflammatory arthritis, and psoriasis: systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Med. 2024 Oct 28;3(1):e000998. doi: 10.1136/bmjmed-2024-000998. eCollection 2024. BMJ Med. 2024. PMID: 39574425 Free PMC article.
-
Adalimumab serum levels and anti-drug antibodies: associations to treatment response and drug survival in inflammatory joint diseases.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 May 3;63(6):1746-1755. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead525. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 37773994 Free PMC article.
-
Biologics or Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Who are Insufficient Responders to Conventional Anti-Rheumatic Drugs.Drugs. 2024 Aug;84(8):877-894. doi: 10.1007/s40265-024-02059-8. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38949688 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maini R, St Clair EW, Breedveld F, Furst D, Kalden J, Weisman M, et al. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet. 1999;354(9194):1932–1939. - PubMed
-
- Weinblatt ME, Kremer JM, Bankhurst AD, Bulpitt KJ, Fleischmann RM, Fox RI, et al. A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumor necrosis factor receptor: Fc fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(4):253–259. - PubMed
-
- Keystone EC, Kavanaugh AF, Sharp JT, Tannenbaum H, Hua Y, Teoh LS, et al. Radiographic, clinical, and functional outcomes of treatment with adalimumab (a human anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis receiving concomitant methotrexate therapy: a randomized, placebo-controlled, 52-week trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(5):1400–1411. - PubMed
-
- Thomas SS, Borazan N, Barroso N, Duan L, Taroumian S, Kretzmann B, et al. Comparative immunogenicity of TNF inhibitors: impact on clinical efficacy and tolerability in the management of autoimmune diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BioDrugs. 2015;29(4):241–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

