Dietary acetic acid suppress high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice by altering taurine conjugated bile acids metabolism
- PMID: 36312883
- PMCID: PMC9596597
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.10.021
Dietary acetic acid suppress high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice by altering taurine conjugated bile acids metabolism
Abstract
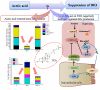
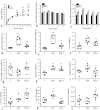
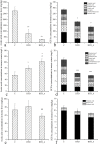
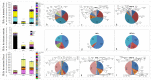
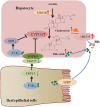
Vinegar is widely used in Chinese diet as a traditional condiment, and its functional component acetic acid has been proposed to prevent obesity, while its mechanism is still unclear. Bile acids (BAs) have been reported to have a protective effect on obesity. This study demonstrated that high-fat diet induced obesity (DIO) seriously disturbed BAs balance by significantly decreasing hepatic BAs synthesis and increasing fecal BAs excretion. However, acetate supplemented in the high-fat diet can restore BAs balance by mainly promoting hepatic taurine conjugated BAs (tauro-BAs) synthesis and decreasing fecal tauro-BAs excretion. The tauro-BAs, as the antagonists, inhibited the intestinal-liver farnesoid X receptor (FXR)-fibroblast growth factor 15 (FGF15)-FGF receptor 4 (FGFR4) signaling pathway, and negatively regulated the production of hepatic BAs. Present study provided important clues for further investigation of the mechanism of acetic acid inhibiting DIO.
Keywords: Acetic acid; Antagonist; Bile acids; FXR; Obesity.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bile acids contribute to the development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice.JHEP Rep. 2021 Oct 13;4(1):100387. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100387. eCollection 2022 Jan. JHEP Rep. 2021. PMID: 34825156 Free PMC article.
-
Penthorum chinense Pursh. extract attenuates non-alcholic fatty liver disease by regulating gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Aug 10;294:115333. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115333. Epub 2022 Apr 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35500802
-
Hepatic cholesterol accumulation ascribed to the activation of ileum Fxr-Fgf15 pathway inhibiting hepatic Cyp7a1 in high-fat diet-induced obesity rats.Life Sci. 2019 Sep 1;232:116638. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116638. Epub 2019 Jul 6. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31288013
-
Modulation of endothelium-derived nitric oxide production and activity by taurine and taurine-conjugated bile acids.Nitric Oxide. 2020 Jan 1;94:48-53. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2019.10.008. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Nitric Oxide. 2020. PMID: 31669041 Review.
-
Molecular Basis of Bile Acid-FXR-FGF15/19 Signaling Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 27;23(11):6046. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116046. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chitosan-Stabilized Selenium Nanoparticles Alleviate High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) by Modulating the Gut Barrier Function and Microbiota.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Aug 22;15(8):236. doi: 10.3390/jfb15080236. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39194674 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota derived bile acid metabolites maintain the homeostasis of gut and systemic immunity.Front Immunol. 2023 May 15;14:1127743. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1127743. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37256134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production of a Series of Long-Chain Isomaltooligosaccharides from Maltose by Bacillus subtilis AP-1 and Associated Prebiotic Properties.Foods. 2023 Apr 3;12(7):1499. doi: 10.3390/foods12071499. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37048320 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of High-Fat Diet and Exercise on Bone and Bile Acid Metabolism in Rats.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 2;16(11):1744. doi: 10.3390/nu16111744. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892677 Free PMC article.
-
Taurine ameliorates sensorimotor function by inhibiting apoptosis and activating A2 astrocytes in mice after subarachnoid hemorrhage.Amino Acids. 2024 Apr 14;56(1):31. doi: 10.1007/s00726-024-03387-5. Amino Acids. 2024. PMID: 38616233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castillo-Olivares Antonio del., Campos Jose A., Pandak Gregorio William M. The role of α1-fetoprotein transcription factor/LRH-1 in bile acid biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279(16) - PubMed
-
- Besten G.D., Lange K., Havinga R., Dijk T.V., Gerding A., Eunen K.V., Muller M., Groen A.K., Hooiveld G.J., Bakker B.M. Gut-derived short-chain fatty acids are vividly assimilated into host carbohydrates and lipids. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013;305(12):G900–G910. - PubMed
-
- Chiang J.Y., Chen W., Zheng M., Wu Z., Kimmel R., Stroup D. Bile acids and FXR represses cholesterol 7A-hydroxylase (CYP7A1), sterol 12A-hydroxylase (CYP8B1) and sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1), but not oxysterol 7A-hydroxylase (CYP7B1) gene transcription. Gastroenterology. 2000;118(4) A1006-A1006.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

