Molecular regulation after mucosal injury and regeneration in ulcerative colitis
- PMID: 36310594
- PMCID: PMC9606627
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.996057
Molecular regulation after mucosal injury and regeneration in ulcerative colitis
Abstract
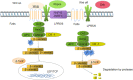
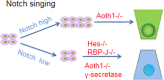
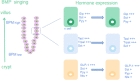
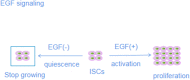
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic nonspecific inflammatory disease with a complex etiology. Intestinal mucosal injury is an important pathological change in individuals with UC. Leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 (LGR5+) intestinal stem cells (ISCs) exhibit self-renewal and high differentiation potential and play important roles in the repair of intestinal mucosal injury. Moreover, LGR5+ ISCs are intricately regulated by both the Wnt/β-catenin and Notch signaling pathways, which jointly maintain the function of LGR5+ ISCs. Combination therapy targeting multiple signaling pathways and transplantation of LGR5+ ISCs may lead to the development of new clinical therapies for UC.
Keywords: intestinal stem cells; molecular regulation; mucosal injury; regeneration; ulcerative colitis.
Copyright © 2022 Zheng, Duan, Wen and Dai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular regulation mechanism of intestinal stem cells in mucosal injury and repair in ulcerative colitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Apr 28;29(16):2380-2396. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i16.2380. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37179583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cooperation of Wnt/β-catenin and Dll1-mediated Notch pathway in Lgr5-positive intestinal stem cells regulates the mucosal injury and repair in DSS-induced colitis mice model.Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2024 Oct 23;12:goae090. doi: 10.1093/gastro/goae090. eCollection 2024. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2024. PMID: 39444950 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-like Factor 5 Regulates Stemness, Lineage Specification, and Regeneration of Intestinal Epithelial Stem Cells.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;9(4):587-609. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.11.009. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31778829 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Cross-regulate NF-κB Signaling in TNF-α-induced Human Lgr5+ Intestinal Stem Cells.Anticancer Res. 2022 Jul;42(7):3325-3340. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.15820. Anticancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35790295
-
The Hippo-YAP/TAZ Signaling Pathway in Intestinal Self-Renewal and Regeneration After Injury.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 19;10:894737. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.894737. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35927987 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of the Notch signalling pathway in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis: from the perspective of intestinal mucosal barrier.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 5;10:1333531. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1333531. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38249980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on the relationship between Paneth cells-susceptibility genes, intestinal microecology and inflammatory bowel disease.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Dec 6;11(34):8111-8125. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i34.8111. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 38130785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances of Wnt Signalling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer.Cells. 2023 Jan 30;12(3):447. doi: 10.3390/cells12030447. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources