The Credible Role of Curcumin in Oxidative Stress-Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Mammals
- PMID: 36291614
- PMCID: PMC9599178
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12101405
The Credible Role of Curcumin in Oxidative Stress-Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Mammals
Abstract
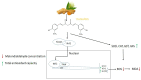
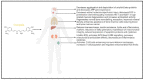
Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction are associated with the pathogenesis of several human diseases. The excessive generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and/or lack of adequate antioxidant defenses causes DNA mutations in mitochondria, damages the mitochondrial respiratory chain, and alters membrane permeability and mitochondrial defense mechanisms. All these alterations are linked to the development of numerous diseases. Curcumin, an active ingredient of turmeric plant rhizomes, exhibits numerous biological activities (i.e., antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and antimicrobial). In recent years, many researchers have shown evidence that curcumin has the ability to reduce the oxidative stress- and mitochondrial dysfunction-associated diseases. In this review, we discuss curcumin's antioxidant mechanism and significance in oxidative stress reduction and suppression of mitochondrial dysfunction in mammals. We also discuss the research gaps and give our opinion on how curcumin research in mammals should proceed moving forward.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; anticancer; antimicrobial; antioxidant; curcumin; mammals; mitochondrial dysfunction; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Curcumin improves hypoxia induced dysfunctions in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by protecting mitochondria and down regulating inflammation.Biofactors. 2014 Sep-Oct;40(5):513-23. doi: 10.1002/biof.1175. Epub 2014 Aug 11. Biofactors. 2014. PMID: 25110893
-
Curcumin ameliorates rabbits's steatohepatitis via respiratory chain, oxidative stress, and TNF-alpha.Free Radic Biol Med. 2009 Oct 1;47(7):924-31. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.06.015. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009. PMID: 19539747
-
Indispensable role of mitochondria in maintaining the therapeutic potential of curcumin in acute kidney injury.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Oct;25(20):9863-9877. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16934. Epub 2021 Sep 16. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34532973 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin Derivatives Linked to a Reduction of Oxidative Stress in Mental Dysfunctions and Inflammatory Disorders.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(41):6826-6841. doi: 10.2174/0929867331666230821102431. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37605400 Review.
-
Mitochondria as a target in the therapeutic properties of curcumin.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2014 Dec;347(12):873-84. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201400266. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2014. PMID: 25243820 Review.
Cited by
-
The Bright Side of Curcumin: A Narrative Review of Its Therapeutic Potential in Cancer Management.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;16(14):2580. doi: 10.3390/cancers16142580. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the Effects of Curcumin and 450 nm Photodynamic Therapy on Oxidative Metabolism and Cell Cycle in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An In Vitro Study.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 24;16(9):1642. doi: 10.3390/cancers16091642. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38730594 Free PMC article.
-
Novel strategies in Parkinson's disease treatment: a review.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Aug 9;17:1431079. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1431079. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39183754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reactive oxygen species-scavenging nanomaterials for the prevention and treatment of age-related diseases.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 May 15;22(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02501-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38750509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin: A Golden Approach to Healthy Aging: A Systematic Review of the Evidence.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 15;16(16):2721. doi: 10.3390/nu16162721. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39203857 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

