Recent Advances of Representative Optical Biosensors for Rapid and Sensitive Diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 36291001
- PMCID: PMC9599922
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12100862
Recent Advances of Representative Optical Biosensors for Rapid and Sensitive Diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
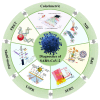
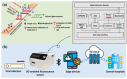
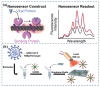
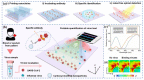
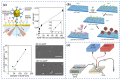
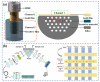
The outbreak of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has again emphasized the significance of developing rapid and highly sensitive testing tools for quickly identifying infected patients. Although the current reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) diagnostic techniques can satisfy the required sensitivity and specificity, the inherent disadvantages with time-consuming, sophisticated equipment and professional operators limit its application scopes. Compared with traditional detection techniques, optical biosensors based on nanomaterials/nanostructures have received much interest in the detection of SARS-CoV-2 due to the high sensitivity, high accuracy, and fast response. In this review, the research progress on optical biosensors in SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis, including fluorescence biosensors, colorimetric biosensors, Surface Enhancement Raman Scattering (SERS) biosensors, and Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) biosensors, was comprehensively summarized. Further, promising strategies to improve optical biosensors are also explained. Optical biosensors can not only realize the rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 but also be applied to judge the infectiousness of the virus and guide the choice of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, showing enormous potential to become point-of-care detection tools for the timely control of the pandemic.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 detection; optical biosensors; point-of-care diagnostics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Biosensors as a future diagnostic approach for COVID-19.Life Sci. 2021 May 15;273:119117. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119117. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33508293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optical biosensors for diagnosis of COVID-19: nanomaterial-enabled particle strategies for post pandemic era.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 May 10;191(6):320. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06373-6. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38727849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optical Biosensors for Virus Detection: Prospects for SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19.Chembiochem. 2021 Apr 6;22(7):1176-1189. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202000744. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Chembiochem. 2021. PMID: 33119960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Nanophotonic Label-Free Biosensors Can Contribute to Rapid and Massive Diagnostics of Respiratory Virus Infections: COVID-19 Case.ACS Sens. 2020 Sep 25;5(9):2663-2678. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.0c01180. Epub 2020 Aug 24. ACS Sens. 2020. PMID: 32786383 Review.
-
Low-Cost Biosensor Technologies for Rapid Detection of COVID-19 and Future Pandemics.ACS Nano. 2024 Jan 23;18(3):1757-1777. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c01629. Epub 2024 Jan 8. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 38189684 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein and Receptor Binding Domain by a Multi-Area Reflectance Spectroscopy Sensor.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 1;13(9):865. doi: 10.3390/bios13090865. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754099 Free PMC article.
-
Two-Dimensional (2D) materials in the detection of SARS-CoV-2.Microchem J. 2023 Oct;193:108970. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2023.108970. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Microchem J. 2023. PMID: 37342763 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplexed Biosensing of Proteins and Virions with Disposable Plasmonic Assays.ACS Sens. 2023 Sep 22;8(9):3338-3348. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.2c02238. Epub 2023 Aug 23. ACS Sens. 2023. PMID: 37610841 Free PMC article.
-
A Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy-Based Biosensor for the Detection of Biological Macromolecules: The Case of the Lipopolysaccharide Endotoxin Molecules.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 28;24(15):12099. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512099. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569474 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation and comparison of one-step real-time PCR and one-step RT-LAMP methods for detection of SARS-CoV-2.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jul 9;24(1):679. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09574-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38982392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Orooji Y., Sohrabi H., Hemmat N., Oroojalian F., Baradaran B., Mokhtarzadeh A., Mohaghegh M., Karimi-Maleh H. An overview on SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) and other human coronaviruses and their detection capability via amplification assay, chemical sensing, biosensing, immunosensing, and clinical assays. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021;13:18. doi: 10.1007/s40820-020-00533-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

