Broadening the Horizons of RNA Delivery Strategies in Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 36290544
- PMCID: PMC9598637
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering9100576
Broadening the Horizons of RNA Delivery Strategies in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
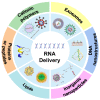
RNA-based therapy is a promising and innovative strategy for cancer treatment. However, poor stability, immunogenicity, low cellular uptake rate, and difficulty in endosomal escape are considered the major obstacles in the cancer therapy process, severely limiting the development of clinical translation and application. For efficient and safe transport of RNA into cancer cells, it usually needs to be packaged in appropriate carriers so that it can be taken up by the target cells and then be released to the specific location to perform its function. In this review, we will focus on up-to-date insights of the RNA-based delivery carrier and comprehensively describe its application in cancer therapy. We briefly discuss delivery obstacles in RNA-mediated cancer therapy and summarize the advantages and disadvantages of different carriers (cationic polymers, inorganic nanoparticles, lipids, etc.). In addition, we further summarize and discuss the current RNA therapeutic strategies approved for clinical use. A comprehensive overview of various carriers and emerging delivery strategies for RNA delivery, as well as the current status of clinical applications and practice of RNA medicines are classified and integrated to inspire fresh ideas and breakthroughs.
Keywords: RNA delivery; cancer therapy; clinical practice; delivery carrier.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nanoparticles-Based Strategies to Improve the Delivery of Therapeutic Small Interfering RNA in Precision Oncology.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jul 29;14(8):1586. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081586. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36015212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleic acid delivery: the missing pieces of the puzzle?Acc Chem Res. 2012 Jul 17;45(7):1153-62. doi: 10.1021/ar3000162. Epub 2012 Mar 19. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22428908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overcoming obstacles in microRNA delivery towards improved cancer therapy.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2014 Feb;4(1):38-49. doi: 10.1007/s13346-013-0160-0. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2014. PMID: 25786616
-
Bioinspired Lipid Nanocarriers for RNA Delivery.ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2023 Jan 16;3(2):114-136. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.2c00073. eCollection 2023 Apr 19. ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2023. PMID: 37101812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent progress in development of siRNA delivery vehicles for cancer therapy.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Sep 1;104:61-77. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.06.011. Epub 2016 Jun 25. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 27352638 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioengineered nanotechnology for nucleic acid delivery.J Control Release. 2023 Dec;364:124-141. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.10.034. Epub 2023 Oct 27. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 37879440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Vaccines: Yeast as a Novel Antigen Vehicle.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Aug 7;11(8):1334. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11081334. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631902 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

