Isoform-specific inhibition of FGFR signaling achieved by a de-novo-designed mini-protein
- PMID: 36288716
- PMCID: PMC9636537
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111545
Isoform-specific inhibition of FGFR signaling achieved by a de-novo-designed mini-protein
Abstract
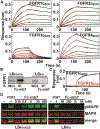
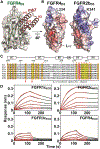
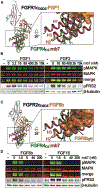
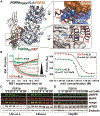
Cellular signaling by fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) is a highly regulated process mediated by specific interactions between distinct subsets of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) ligands and two FGFR isoforms generated by alternative splicing: an epithelial b- and mesenchymal c-isoforms. Here, we investigate the properties of a mini-protein, mb7, developed by an in silico design strategy to bind to the ligand-binding region of FGFR2. We describe structural, biophysical, and cellular analyses demonstrating that mb7 binds with high affinity to the c-isoforms of FGFR, resulting in inhibition of cellular signaling induced by a subset of FGFs that preferentially activate c-isoforms of FGFR. Notably, as mb7 blocks interaction between FGFR with Klotho proteins, it functions as an antagonist of the metabolic hormones FGF19 and FGF21, providing mechanistic insights and strategies for the development of therapeutics for diseases driven by aberrantly activated FGFRs.
Keywords: CP: Cell biology; cell signaling; de novo protein design; fibroblast growth factors; protein structure; receptor tyrosine kinase.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Klotho coreceptors inhibit signaling by paracrine fibroblast growth factor 8 subfamily ligands.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 May;32(10):1944-54. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06603-11. Epub 2012 Mar 26. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22451487 Free PMC article.
-
Isoforms of receptors of fibroblast growth factors.J Cell Physiol. 2014 Dec;229(12):1887-95. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24649. J Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24733629 Review.
-
Structures of β-klotho reveal a 'zip code'-like mechanism for endocrine FGF signalling.Nature. 2018 Jan 25;553(7689):501-505. doi: 10.1038/nature25010. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29342135 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of residues important both for primary receptor binding and specificity in fibroblast growth factor-7.J Biol Chem. 2000 Nov 10;275(45):34881-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003293200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10950949
-
Non-canonical fibroblast growth factor signalling in angiogenesis.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 May 1;78(2):223-31. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvm086. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18056763 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting overexpressed antigens in glioblastoma via CAR T cells with computationally designed high-affinity protein binders.Nat Biomed Eng. 2024 Dec;8(12):1634-1650. doi: 10.1038/s41551-024-01258-8. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Nat Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 39420062
-
Peptides of a Feather: How Computation Is Taking Peptide Therapeutics under Its Wing.Genes (Basel). 2023 May 29;14(6):1194. doi: 10.3390/genes14061194. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of FGF pathway signaling and vascular differentiation using designed oligomeric assemblies.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 15:2023.03.14.532666. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.14.532666. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cell. 2024 Jul 11;187(14):3726-3740.e43. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.05.025 PMID: 36993355 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Modulation of FGF pathway signaling and vascular differentiation using designed oligomeric assemblies.Cell. 2024 Jul 11;187(14):3726-3740.e43. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.05.025. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Cell. 2024. PMID: 38861993
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

