Mechanism of action of CTRP6 in the regulation of tumorigenesis in the digestive system
- PMID: 36276484
- PMCID: PMC9533366
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2022.13511
Mechanism of action of CTRP6 in the regulation of tumorigenesis in the digestive system
Abstract
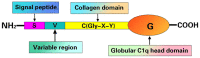
Tumors of the digestive system have always received attention, and their occurrence and development are regulated by various mechanisms such as inflammation and immunity, glucose and lipid metabolism, and tumor angiogenesis. Complement Clq/TNF-related protein 6 (CTRP6) is a member of the CTRP family; it is widely expressed in various tissues and cell types, and plays a biological role in a number of mechanisms, such as glucose and lipid metabolism and inflammation. Recent studies have revealed the tumor-promoting effect of CTRP6 in gastric cancer, liver cancer, colorectal cancer and other gastrointestinal tumors, but, to the best of our knowledge, there has been no systematic discussion on the tumor-promoting mechanism of CTRP6. The present study reviews the role of CTRP6 in tumors of the digestive system and its possible mechanisms.
Keywords: C1qTNF-related protein 6; colon cancer; gastric cancer; protein kinase B.
Copyright: © Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor-related factor complement Clq/TNF-related protein 6 affects the development of digestive system tumors through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Jul 14;30(26):3206-3209. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i26.3206. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39086639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the functions of CTRP6 in the development and progression of the malignancy.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 12;13:985077. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.985077. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36313428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C1q/TNF-Related Protein 6 Is a Pattern Recognition Molecule That Recruits Collectin-11 from the Complement System to Ligands.J Immunol. 2020 Mar 15;204(6):1598-1606. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901316. Epub 2020 Feb 10. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32041782
-
Molecular, biochemical and functional characterizations of C1q/TNF family members: adipose-tissue-selective expression patterns, regulation by PPAR-gamma agonist, cysteine-mediated oligomerizations, combinatorial associations and metabolic functions.Biochem J. 2008 Dec 1;416(2):161-77. doi: 10.1042/BJ20081240. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18783346 Free PMC article.
-
C1q/TNF-related protein 6 (CTRP6) links obesity to adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance.J Biol Chem. 2017 Sep 8;292(36):14836-14850. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.766808. Epub 2017 Jul 18. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28726640 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Tumor-related factor complement Clq/TNF-related protein 6 affects the development of digestive system tumors through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Jul 14;30(26):3206-3209. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i26.3206. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39086639 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang CL, Wu LL, Li L. Research progress of complement-C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein 3. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2017;69:666–676. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Liu Z, Duan L, Ma B, Sun Z. C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein 6 (CTRP6) inhibits the proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015;31:1664–1668. (In Chinese) - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
