Clinical features of patients with talaromycosis marneffei and microbiological characteristics of the causative strains
- PMID: 36268985
- PMCID: PMC9701894
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24737
Clinical features of patients with talaromycosis marneffei and microbiological characteristics of the causative strains
Abstract
Background: Talaromyces marneffei (T. marneffei) is a temperature-dependent dimorphic fungus that is mainly prevalent in Southeast Asia and South China and often causes disseminated life-threatening infections. This study aimed to investigate the clinical features and improve the early diagnosis of talaromycosis marneffei in nonendemic areas.
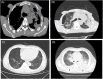
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the medical records of six cases of T. marneffei infection. We describe the clinical manifestations, laboratory tests, and imaging manifestations of the six patients.
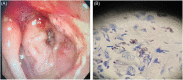
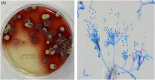
Results: Talaromyces marneffei infection was confirmed by sputum culture, blood culture, tissue biopsy, and metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS). In this study, there were five disseminated-type patients and two HIV patients. One patient died within 24 h, and the others demonstrated considerable improvement after definitive diagnosis.
Conclusions: Due to the lack of significant clinical presentations of talaromycosis marneffei, many cases may be easily misdiagnosed in nonendemic areas. It is particularly important to analyze the imaging manifestations and laboratory findings of infected patients. With the rapid development of molecular biology, mNGS may be a rapid and effective diagnostic method.
Keywords: Talaromyces marneffei; disseminated Talaromyces marneffei infection; laboratory test; metagenomic next-generation sequencing; talaromycosis marneffei.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical usefulness of metagenomic next-generation sequencing for Talaromyces marneffei diagnosis in China: a retrospective study.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024 Jul;43(7):1367-1374. doi: 10.1007/s10096-024-04856-1. Epub 2024 May 27. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38801485
-
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing for the early diagnosis of talaromycosis in HIV-uninfected patients: five cases report.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Aug 23;21(1):865. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06551-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34425764 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid diagnosis of Talaromyces marneffei infection by metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in a Chinese cohort of inborn errors of immunity.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Sep 8;12:987692. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.987692. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36159645 Free PMC article.
-
Talaromycosis (Penicilliosis) Due to Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei: Insights into the Clinical Trends of a Major Fungal Disease 60 Years After the Discovery of the Pathogen.Mycopathologia. 2019 Dec;184(6):709-720. doi: 10.1007/s11046-019-00410-2. Mycopathologia. 2019. PMID: 31811603 Review.
-
Diagnostic laboratory immunology for talaromycosis (penicilliosis): review from the bench-top techniques to the point-of-care testing.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020 Mar;96(3):114959. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2019.114959. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31836254 Review.
Cited by
-
Coexisting of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma and Talaromyces marneffei Brain Abscess in an AIDS Patient, A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Feb 22;17:709-718. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S432697. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38410795 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary hemophagocytic syndrome in an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and Alpha-thalassemia patient infected with Talaromyces marneffei: A case report and literature review.IDCases. 2024 Apr 15;36:e01954. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2024.e01954. eCollection 2024. IDCases. 2024. PMID: 38659622 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Characteristics Associated with Poor Prognosis of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome Patients Complicated with Disseminated Talaromycosis marneffei.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Nov 7;16:7097-7108. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S434695. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37954504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou F, Bi X, Zou X, Xu Z, Zhang T. Retrospective analysis of 15 cases of Penicilliosis marneffei in a southern China hospital. Mycopathologia. 2014;177(5–6):271‐279. - PubMed
-
- Lee PP, Chan KW, Lee TL, et al. Penicilliosis in children without HIV infection—are they immunodeficient? Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54(2):e8‐e19. - PubMed
-
- Hu Y, Zhang J, Li X, et al. Penicillium marneffei infection: an emerging disease in mainland China. Mycopathologia. 2013;175(1–2):57‐67. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

