Prediction of intraoperative bleeding and blood transfusion in patients with recurrent retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a retrospective study
- PMID: 36267785
- PMCID: PMC9577802
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-4222
Prediction of intraoperative bleeding and blood transfusion in patients with recurrent retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Surgery is the main treatment for recurrent retroperitoneal liposarcoma (RPLS). The aim of the present study was to explore the factors associated with blood loss during surgery for recurrent RPLS.
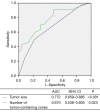
Methods: This retrospective study included patients with first recurrence of RPLS who were treated at our hospital between January 2015 and December 2019. Factors associated with intraoperative blood loss were identified by univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses were conducted to evaluate whether tumor size and number of tumor-containing abdominal/pelvic zones were predictive of the need for blood transfusion.
Results: The study included 67 cases. The number of zones containing tumors was 1 in 4 cases (6%), 2 in 36 cases (53.7%), 3 in 14 cases (20.9%), and 4 in 13 cases (19.4%). Tumor size was associated with blood loss >500 mL [odds ratio (OR): 1.153, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.051-1.266, P=0.003]. The number of tumor-containing zones was associated with blood loss >1,000 mL (OR: 3.161, 95% CI: 1.248-8.003, P=0.015) and >1,500 mL (OR: 2.674, 95% CI: 1.061-6.739, P=0.037). Multiple tumors were associated with blood loss >2,000 mL (OR: 3.161, 95% CI: 1.092-13.133, P=0.036) and >2,500 mL (OR: 2.674, 95% CI: 1.243-16.299, P=0.022). Tumor dedifferentiation was associated with blood loss >1,000 mL (OR: 4.802, 95% CI: 1.287-17.916, P=0.019) and >1,500 mL (OR: 9.249, 95% CI: 1.927-44.39, P=0.005). ROC curve analysis showed that tumor size >15.25 cm [area under the ROC curve (AUC): 0.772, P<0.001] and the number of tumor-containing zones >2.5 (AUC: 0.670; P=0.023) were predictive of the need for blood transfusion.
Conclusions: The main finding of the present study was that a larger tumor size, a larger number of tumor-containing zones, multiple tumors, and dedifferentiation were independently associated with a larger volume of intraoperative blood loss in patients with recurrent RPLS. The tumor size >15.25 cm and the tumor area >2.5 areas predicted the need for blood transfusion. Formulating the intraoperative blood transfusion plan for recurrent RPLS, it is necessary to pay attention to two spatial factors, tumor size and affected area, rather than one of them.
Keywords: Retroperitoneal liposarcoma (RPLS); bleeding; intraoperative blood loss; recurrence; risk factors.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-4222/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of predictors for short-term recurrence: comprehensive analysis of 296 retroperitoneal liposarcoma cases.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Feb 6;22(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03328-2. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38321480 Free PMC article.
-
A better overall survival (OS) for total (ipsilateral) retroperitoneal lipectomy than standard complete resection in patients with retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a comparative multi-institutional study.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Jul;10(14):785. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3332. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35965811 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical experience with retroperitoneal liposarcoma in a single korean tertiary medical center.Korean J Urol. 2012 May;53(5):310-6. doi: 10.4111/kju.2012.53.5.310. Epub 2012 May 18. Korean J Urol. 2012. PMID: 22670189 Free PMC article.
-
Visceral adiposity and inflammatory bowel disease.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021 Nov;36(11):2305-2319. doi: 10.1007/s00384-021-03968-w. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021. PMID: 34104989 Review.
-
Clinicopathological characteristics and experience in the treatment of giant retroperitoneal liposarcoma: A case report and review of the literature.Cancer Biol Ther. 2017 Sep 2;18(9):660-665. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1345388. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Cancer Biol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28758856 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive factors and a novel nomogram for recurrence of primary retroperitoneal liposarcoma: Comprehensive analysis of 128 cases.Oncol Lett. 2023 Apr 28;25(6):257. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13843. eCollection 2023 Jun. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37485421 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning algorithms to predict intraoperative hemorrhage in surgical patients: a modeling study of real-world data in Shanghai, China.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023 Aug 10;23(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12911-023-02253-w. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023. PMID: 37563676 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources