C3G down-regulation enhances pro-migratory and stemness properties of oval cells by promoting an epithelial-mesenchymal-like process
- PMID: 36263169
- PMCID: PMC9576514
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.73192
C3G down-regulation enhances pro-migratory and stemness properties of oval cells by promoting an epithelial-mesenchymal-like process
Abstract
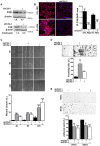
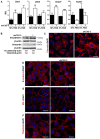
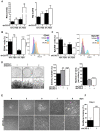
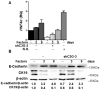
Previous data indicate that C3G (RapGEF1) main isoform is highly expressed in liver progenitor cells (or oval cells) compared to adult mature hepatocytes, suggesting it may play an important role in oval cell biology. Hence, we have explored C3G function in the regulation of oval cell properties by permanent gene silencing using shRNAs. We found that C3G knock-down enhanced migratory and invasive ability of oval cells by promoting a partial epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT). This is likely mediated by upregulation of mRNA expression of the EMT-inducing transcription factors, Snail1, Zeb1 and Zeb2, induced in C3G-silenced oval cells. This EMT is associated to a higher expression of the stemness markers, CD133 and CD44. Moreover, C3G down-regulation increased oval cells clonogenic capacity by enhancing cell scattering. However, C3G knock-down did not impair oval cell differentiation into hepatocyte lineage. Mechanistic studies revealed that HGF/MET signaling and its pro-invasive activity was impaired in oval cells with low levels of C3G, while TGF-β signaling was increased. Altogether, these data suggest that C3G might be tightly regulated to ensure liver repair in chronic liver diseases such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hence, reduced C3G levels could facilitate oval cell expansion, after the proliferation peak, by enhancing migration.
Keywords: C3G; epithelial mesenchymal transition; migration; oval cells; stemness.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
c-Met Signaling Is Essential for Mouse Adult Liver Progenitor Cells Expansion After Transforming Growth Factor-β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Regulates Cell Phenotypic Switch.Stem Cells. 2019 Aug;37(8):1108-1118. doi: 10.1002/stem.3038. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Stem Cells. 2019. PMID: 31108004
-
C3G Is Upregulated in Hepatocarcinoma, Contributing to Tumor Growth and Progression and to HGF/MET Pathway Activation.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 14;12(8):2282. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082282. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32823931 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β-induced plasticity causes a migratory stemness phenotype in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2017 Apr 28;392:39-50. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.01.037. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28161507
-
HGF/c-Met signaling promotes liver progenitor cell migration and invasion by an epithelial-mesenchymal transition-independent, phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase-dependent pathway in an in vitro model.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1853(10 Pt A):2453-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.05.017. Epub 2015 May 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26001768
-
[Aberrant Activation Mechanism of TGF-β Signaling in Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2021;141(11):1229-1234. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.21-00143. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2021. PMID: 34719542 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
New and Old Key Players in Liver Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 5;24(24):17152. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417152. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38138981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cepharanthine inhibits migration, invasion, and EMT of bladder cancer cells by activating the Rap1 signaling pathway in vitro.Am J Transl Res. 2024 May 15;16(5):1602-1619. doi: 10.62347/WDFF7432. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38883391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- del Castillo G, Alvarez-Barrientos A, Carmona-Cuenca I, Fernandez M, Sanchez A, Fabregat I. Isolation and characterization of a putative liver progenitor population after treatment of fetal rat hepatocytes with TGF-beta. Journal of cellular physiology. 2008;215:846–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

