Immunization with HIV-1 trimeric SOSIP.664 BG505 or founder virus C (FVCEnv) covalently complexed to two-domain CD4S60C elicits cross-clade neutralizing antibodies in New Zealand white rabbits
- PMID: 36262212
- PMCID: PMC9573916
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2022.100222
Immunization with HIV-1 trimeric SOSIP.664 BG505 or founder virus C (FVCEnv) covalently complexed to two-domain CD4S60C elicits cross-clade neutralizing antibodies in New Zealand white rabbits
Abstract
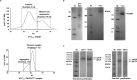
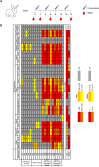
Background: An ongoing challenge in HIV-1 vaccine research is finding a novel HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (Env)-based immunogen that elicits broadly cross-neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) without requiring complex sequential immunization regimens to drive the required antibody affinity maturation. Previous vaccination studies have shown monomeric Env and Env trimers which contain the GCN4 leucine zipper trimerization domain and are covalently bound to the first two domains of CD4 (2dCD4S60C) generate potent bnAbs in small animals. Since SOSIP.664 trimers are considered the most accurate, conformationally intact representation of HIV-1 Env generated to date, this study further evaluated the immunogenicity of SOSIP.664 HIV Env trimers (the well characterized BG505 and FVCEnv) covalently complexed to 2dCD4S60C. Methods: Recombinant BG505 SOSIP.664 and FVCEnv SOSIP.664 were expressed in mammalian cells, purified, covalently coupled to 2dCD4S60C and antigenically characterized for their interaction with HIV-1 bnAbs. The immunogenicity of BG505 SOSIP.664-2dCD4S60C and FVCEnv SOSIP.664-2dCD4S60C was investigated in New Zealand white rabbits and compared to unliganded FVCEnv and 2dCD4S60C. Rabbit sera were tested for the presence of neutralizing antibodies against a panel of 17 pseudoviruses. Results: Both BG505 SOSIP.664-2dCD4S60C and FVCEnv SOSIP.664-2dCD4S60C elicited a potent, HIV-specific response in rabbits with antibodies having considerable potency and breadth (70.5% and 76%, respectively) when tested against a global panel of 17 pseudoviruses mainly composed of harder-to-neutralize multiple clade tier-2 pseudoviruses. Conclusion: BG505 SOSIP.664-2dCD4S60C and FVCEnvSOSIP.664-2dCD4S60C are highly immunogenic and elicit potent, broadly neutralizing antibodies, the extent of which has never been reported previously for SOSIP.664 trimers. Adding to our previous results, the ability to consistently elicit these types of potent, cross-neutralizing antibody responses is dependent on novel epitopes exposed following the covalent binding of Env (independent of sequence and conformation) to 2dCD4S60C. These findings justify further investment into research exploring modified open, CD4-bound Env conformations as novel vaccine immunogens.
Keywords: Broadly neutralizing antibodies; Covalent complexes; Envelope glycoprotein trimers; HIV-1 vaccine immunogens; Immunogen design; New Zealand White rabbits.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Env-2dCD4 S60C complexes act as super immunogens and elicit potent, broadly neutralizing antibodies against clinically relevant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1).Vaccine. 2015 Nov 17;33(46):6298-306. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.09.056. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26432912
-
Covalent binding of human two-domain CD4 to an HIV-1 subtype C SOSIP.664 trimer modulates its structural dynamics.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Jul 5;612:181-187. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.04.101. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 35550505
-
Immunogenicity of a Prefusion HIV-1 Envelope Trimer in Complex with a Quaternary-Structure-Specific Antibody.J Virol. 2015 Dec 30;90(6):2740-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02380-15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26719262 Free PMC article.
-
The HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein structure: nailing down a moving target.Immunol Rev. 2017 Jan;275(1):21-32. doi: 10.1111/imr.12507. Immunol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28133813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficiently cleaved HIV-1 envelopes: can they be important for vaccine immunogen development?Ther Adv Vaccines Immunother. 2020 Oct 8;8:2515135520957763. doi: 10.1177/2515135520957763. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Vaccines Immunother. 2020. PMID: 33103053 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring synergies between B- and T-cell vaccine approaches to optimize immune responses against HIV-workshop report.NPJ Vaccines. 2024 Feb 21;9(1):39. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-00818-y. NPJ Vaccines. 2024. PMID: 38383616 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA-based HIV-1 vaccines.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024 Sep 12;37(3):e0004124. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00041-24. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39016564 Review.
References
-
- UNAIDS. Fact sheet - Global HIV & AIDS statistics - 2021 fact sheet. 2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

