Thirty-six months recurrence after acute ischemic stroke among patients with comorbid type 2 diabetes: A nested case-control study
- PMID: 36248006
- PMCID: PMC9562049
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.999568
Thirty-six months recurrence after acute ischemic stroke among patients with comorbid type 2 diabetes: A nested case-control study
Abstract
Background: Stroke patients have to face a high risk of recurrence, especially for those with comorbid T2DM, which usually lead to much more serious neurologic damage and an increased likelihood of death. This study aimed to explore determinants of stroke relapse among patients with comorbid T2DM.
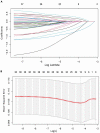
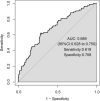
Materials and methods: We conducted this case-control study nested a prospective cohort of ischemic stroke (IS) with comorbid T2DM. During 36-month follow-up, the second stroke occurred in 84 diabetic IS patients who were allocated into the case group, while 613 patients without recurrence were the controls. We collected the demographic data, behaviors and habits, therapies, and family history at baseline, and measured the variables during follow-up. LASSO and Logistic regression analyses were carried out to develop a prediction model of stroke recurrence. The receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve was employed to evaluate the performance of the prediction model.
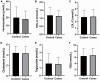
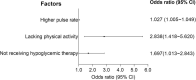
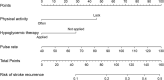
Results: Compared to participants without recurrence, the higher levels of pulse rate (78.29 ± 12.79 vs. 74.88 ± 10.93) and hypertension (72.6 vs. 61.2%) were recorded at baseline. Moreover, a lower level of physical activity (77.4 vs. 90.4%), as well as a higher proportion of hypoglycemic therapy (36.9 vs. 23.3%) was also observed during 36-month follow-up. Multivariate logistic regression revealed that higher pulse rate at admission (OR = 1.027, 95 %CI = 1.005-1.049), lacking physical activity (OR = 2.838, 95% CI = 1.418-5.620) and not receiving hypoglycemic therapy (OR = 1.697, 95% CI = 1.013-2.843) during follow-up increased the risk of stroke recurrence. We developed a prediction model using baseline pulse rate, hypoglycemic therapy, and physical activity, which produced an area under ROC curve (AUC) of 0.689.
Conclusion: Physical activity and hypoglycemic therapy play a protective role for IS patients with comorbid diabetes. In addition to targeted therapeutics, the improvement of daily-life habit contributes to slowing the progress of the IS.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; ischemic stroke; nested case-control study; recurrence; risk factors.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Li, Hao, Liu, Wang, Feng, Guo, Zheng, Zhang, Li, Zhang and Hou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive value of the combination between the intracranial arterial culprit plaque characteristics and the Essen Stroke Risk Score for short-term stroke recurrence.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022 Sep;31(9):106624. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2022.106624. Epub 2022 Aug 4. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022. PMID: 35933933
-
Acute Ischemic Stroke Comorbid with Type 2 Diabetes: Long-Term Prognosis Determinants in a 36-Month Prospective Study for Personalized Medicine.OMICS. 2022 Aug;26(8):451-460. doi: 10.1089/omi.2022.0071. Epub 2022 Aug 2. OMICS. 2022. PMID: 35917518
-
Functional outcome prediction of ischemic stroke patients with atrial fibrillation accepting post-acute care training.Front Neurol. 2022 Sep 23;13:954212. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.954212. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36212653 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A is a stronger predictor for adverse cardiovascular outcomes after acute coronary syndrome in type-2 diabetes mellitus.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017 Apr 5;16(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0526-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017. PMID: 28381225 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of pioglitazone in acute ischemic stroke patients with diabetes mellitus: a nested case-control study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019 May 31;18(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0874-5. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019. PMID: 31151454 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The association between total bile acid and bone mineral density among patients with type 2 diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 24;14:1153205. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1153205. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37033244 Free PMC article.
-
Post-stroke experiences and health information needs among Chinese elderly ischemic stroke survivors in the internet environment: a qualitative study.Front Psychol. 2023 Aug 16;14:1150369. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1150369. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37663326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armangue T., Spatola M., Vlagea A., Mattozzi S., Cárceles-Cordon M., Martinez-Heras E., et al. (2018). Frequency, symptoms, risk factors, and outcomes of autoimmune encephalitis after herpes simplex encephalitis: A prospective observational study and retrospective analysis. Lancet Neurol. 17 760–772. 10.1016/s1474-4422(18)30244-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

