An expanded population of CD8dim T cells with features of mitochondrial dysfunction and senescence is associated with persistent HIV-associated Kaposi's sarcoma under ART
- PMID: 36247006
- PMCID: PMC9557199
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.961021
An expanded population of CD8dim T cells with features of mitochondrial dysfunction and senescence is associated with persistent HIV-associated Kaposi's sarcoma under ART
Abstract
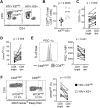
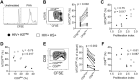
HIV-associated Kaposi's sarcoma (KS), which is caused by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, usually arises in the context of uncontrolled HIV replication and immunosuppression. However, disease occasionally occurs in individuals with durable HIV viral suppression and CD4 T cell recovery under antiretroviral therapy (ART). The underlying mechanisms associated with this phenomenon are unclear. Suppression of viral infections can be mediated by CD8 T cells, which detect infected cells via their T cell receptor and the CD8 coreceptor. However, CD8 T cells exhibit signs of functional exhaustion in untreated HIV infection that may not be fully reversed under ART. To investigate whether KS under ART was associated with phenotypic and functional perturbations of CD8 T cells, we performed a cross-sectional study comparing HIV-infected individuals with persistent KS under effective ART (HIV+ KS+) to HIV-infected individuals receiving effective ART with no documented history of KS (HIV+ KSneg). A subset of T cells with low cell surface expression of CD8 ("CD8dim T cells") was expanded in HIV+ KS+ compared with HIV+ KSneg participants. Relative to CD8bright T cells, CD8dim T cells exhibited signs of senescence (CD57) and mitochondrial alterations (PGC-1α, MitoTracker) ex vivo. Mitochondrial activity (MitoTracker) was also reduced in proliferating CD8dim T cells. These findings indicate that an expanded CD8dim T cell population displaying features of senescence and mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with KS disease under ART. CD8 coreceptor down-modulation may be symptomatic of ongoing disease.
Keywords: CD8 coreceptor; HIV; KSHV; Kaposi’s sarcoma; T cells; metabolism; mitochondria; senescence.
Copyright © 2022 Clutton, Weideman, Goonetilleke and Maurer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lack of CD8+ T-cell co-localization with Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infected cells in Kaposi's sarcoma tumors.Oncotarget. 2020 Apr 28;11(17):1556-1572. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27569. eCollection 2020 Apr 28. Oncotarget. 2020. PMID: 32391124 Free PMC article.
-
Restricted Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) herpesvirus transcription in KS lesions from patients on successful antiretroviral therapy.mBio. 2011 Nov 1;2(6):e00138-11. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00138-11. Print 2011. mBio. 2011. PMID: 22045987 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus in peripheral blood cells in human immunodeficiency virus infection: association with Kaposi's sarcoma, CD4 cell count, and HIV RNA levels.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1999 Jan 1;15(1):51-5. doi: 10.1089/088922299311709. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1999. PMID: 10024052
-
Epidemiology of Kaposi's sarcoma in sub-Saharan Africa.Cancer Epidemiol. 2022 Jun;78:102167. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2022.102167. Epub 2022 Apr 30. Cancer Epidemiol. 2022. PMID: 35504064 Review.
-
Cellular origin of Kaposi's sarcoma and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-induced cell reprogramming.Trends Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;23(9):421-32. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 May 17. Trends Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23685018 Review.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 patients display changes in lymphocyte subsets with a higher frequency of dysfunctional CD8lo T cells associated with disease severity.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 21;14:1223730. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1223730. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37809093 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bengsch B., Johnson A. L., Kurachi M., Odorizzi P. M., Pauken K. E., Attanasio J., et al. (2016). Bioenergetic insufficiencies due to metabolic alterations regulated by the inhibitory receptor PD-1 are an early driver of CD8+ T cell exhaustion. Immunity 45, 358–373. 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.07.008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bihl F., Narayan M., Chisholm J. V., Henry L. M., Suscovich T. J., Brown E. E., et al. (2007). Lytic and latent antigens of the human gammaherpesviruses Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and Epstein-Barr virus induce T-cell responses with similar functional properties and memory phenotypes. J. Virol. 81, 4904–4908. 10.1128/jvi.02509-06 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

