Systematic Analysis of CXC Chemokine-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A Network in Colonic Adenocarcinoma from the Perspective of Angiogenesis
- PMID: 36246978
- PMCID: PMC9553499
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5137301
Systematic Analysis of CXC Chemokine-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A Network in Colonic Adenocarcinoma from the Perspective of Angiogenesis
Abstract
Background: Tumor angiogenesis plays a vital role in tumorigenesis, proliferation, and metastasis. Recently, vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and CXC chemokines have been shown to play vital roles in angiogenesis. Exploring the expression level, gene regulatory network, prognostic value, and target prediction of the CXC chemokine-VEGFA network in colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) is crucial from the perspective of tumor angiogenesis.
Methods: In this study, we analyzed gene expression and regulation, prognostic value, target prediction, and immune infiltrates related to the CXC chemokine-VEGFA network in patients with COAD using multiple databases (cBioPortal, UALCAN, Human Protein Atlas, GeneMANIA, GEPIA, TIMER (version 2.0), TRRUST (version 2), LinkedOmics, and Metascape).
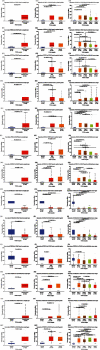
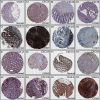
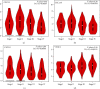
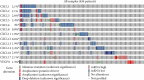
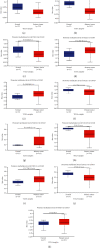
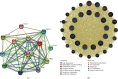
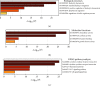
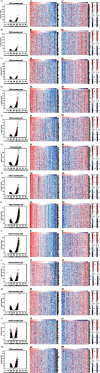
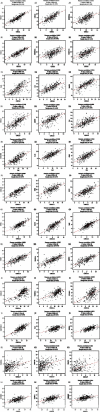
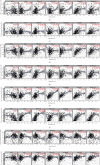
Results: Our results showed that CXCL1/2/3/5/6/8/11/16/17 and VEGFA were markedly overexpressed, while CXCL12/13/14 were underexpressed in patients with COAD. Moreover, genetic alterations in the CXC chemokine-VEGFA network found at varying rates in patients with COAD were as follows: CXCL1/2/17 (2.1%), CXCL3/16 (2.6%), CXCL5/14 (2.4%), CXCL6 (3%), CXCL8 (0.8%), CXCL11/13 (1.9%), CXCL12 (0.6%), and VEGFA (1.3%). Promoter methylation of CXCL1/2/3/11/13/17 was considerably lower in patients with COAD, whereas methylation of CXCL5/6/12/14 and VEGFA was considerably higher. Furthermore, CXCL9/10/11 and VEGFA expression was notably correlated with the pathological stages of COAD. In addition, patients with COAD with high CXCL8/11/14 or low VEGFA expression levels survived longer than patients with dissimilar expression levels. CXC chemokines and VEGFA form a complex regulatory network through coexpression, colocalization, and genetic interactions. Moreover, many transcription factor targets of the CXC chemokine-VEGFA network in patients with COAD were identified: RELA, NFKB1, ZFP36, XBP1, HDAC2, SP1, ATF4, EP300, BRCA1, ESR1, HIF1A, EGR1, STAT3, and JUN. We further identified the top three miRNAs involved in regulating each CXC chemokine within the network: miR-518C, miR-369-3P, and miR-448 regulated CXCL1; miR-518C, miR-218, and miR-493 regulated CXCL2; miR-448, miR-369-3P, and miR-221 regulated CXCL3; miR-423 regulated CXCL13; miR-378, miR-381, and miR-210 regulated CXCL14; miR-369-3P, miR-382, and miR-208 regulated CXCL17; miR-486 and miR-199A regulated VEGFA. Furthermore, the CXC chemokine-VEGFA network in patients with COAD was notably associated with immune infiltration.
Conclusions: This study revealed that the CXC chemokine-VEGFA network might act as a prognostic biomarker for patients with COAD. Moreover, our study provides new therapeutic targets for COAD, serving as a reference for further research in the future.
Copyright © 2022 Yongli Situ et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploration of prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets in the microenvironment of bladder cancer based on CXC chemokines.Math Biosci Eng. 2021 Jul 19;18(5):6262-6287. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2021313. Math Biosci Eng. 2021. PMID: 34517533
-
System analysis of VEGFA in renal cell carcinoma: The expression, prognosis, gene regulation network and regulation targets.Int J Biol Markers. 2022 Mar;37(1):90-101. doi: 10.1177/17246008211063501. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Int J Biol Markers. 2022. PMID: 34870494
-
Elevated expression of CXCL3 in colon cancer promotes malignant behaviors of tumor cells in an ERK-dependent manner.BMC Cancer. 2023 Nov 29;23(1):1162. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11655-y. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38031087 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Hypoxia on the Expression of CXC Chemokines and CXC Chemokine Receptors-A Review of Literature.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 15;22(2):843. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020843. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33467722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cryptic role of CXCL17/CXCR8 axis in the pathogenesis of cancers: a review of the latest evidence.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep;17(3):409-422. doi: 10.1007/s12079-022-00699-7. Epub 2022 Nov 9. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36352331 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage Inflammatory Proteins (MIPs) Contribute to Malignant Potential of Colorectal Polyps and Modulate Likelihood of Cancerization Associated with Standard Risk Factors.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 23;25(3):1383. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031383. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338661 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of protein kinase C isozymes causes immune profile alteration and possibly decreased tumorigenesis in bladder cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Aug 15;13(8):3832-3852. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37693140 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Spatial Co-occurrence in Healthy and InflAmed tissues (ISCHIA).Mol Syst Biol. 2024 Feb;20(2):98-119. doi: 10.1038/s44320-023-00006-5. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Mol Syst Biol. 2024. PMID: 38225383 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of VEGF-A expression and VEGF-A-targeted therapy in malignant tumors.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Apr 30;150(5):221. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05714-5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38687357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization and validation of a prognostic model for the N6-methyladenosine-associated ferroptosis gene in colon adenocarcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Aug 31;13(8):4389-4407. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-88. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39262465 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

