Identification and characterization of extrachromosomal circular DNA in alcohol induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- PMID: 36246642
- PMCID: PMC9561878
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.918379
Identification and characterization of extrachromosomal circular DNA in alcohol induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
Abstract
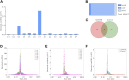
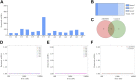
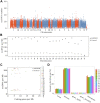
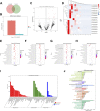
Alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (AIONFH) is a complicated refractory bone disease seen in the clinic. The pathogenesis of AIONFH is still controversial. Extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) elements have been indicated ubiquitously exist in eukaryotic genomes. However, the characteristics and biological functions of eccDNAs remain unclear in AIONFH. In this study, eccDNAs from AIONFH samples (n = 7) and fracture of femoral neck samples as a control (n = 7) were purified by removing linear DNA and rolling circle amplification. High-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis were performed to study the characterization and biofunction of eccDNAs. We identified more than 600,000 unique eccDNAs. The number of detected eccDNAs in AIONFH was less than that in the control, and eccDNA formation may be related to transcription or other characteristics of coding genes. The eccDNA lengths are mainly distributed between 0.1 kb and 1 kb, with a major peak in 0.358 kb. The bioinformatic analysis showed that 25 significant genes were detected, including MAP3K1, ADCY1, CACNA1S, and MACF1, which contributed to regulating bone formation. GO and KEGG analyses suggested that the related genes derived from exons mainly affected metabolic processes and signal transduction, and bone metabolism-related pathways, such as the MAPK pathway and TGF-β pathway, were enriched. EccDNAs in AIONFH are common and may play an important role in pathogenesis by regulating bone metabolism.
Keywords: alcohol induced osteonecrosis of femoral head; bioinformatics; chromosomal instability; extrachromosomal circular DNA; function of eccDNA.
Copyright © 2022 Zhou, Ma, Zhao, Guo, Wang, Kuang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Extrachromosomal circular DNAs are common and functional in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Sep;9(18):1464. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-4372. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34734016 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of extrachromosomal circular DNA in large-artery atherosclerotic stroke.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Apr;28(7):e18210. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18210. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38506071 Free PMC article.
-
The characteristics of extrachromosomal circular DNA in patients with end-stage renal disease.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Mar 27;28(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01064-z. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 36967395 Free PMC article.
-
Extrachromosomal Circular DNAs: Origin, formation and emerging function in Cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Mar 2;17(4):1010-1025. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.54614. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33867825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA): major functions in evolution and cancer.Mol Cancer. 2021 Sep 3;20(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01413-8. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34479546 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the role of extrachromosomal circular DNA in adipose stem cells from old and young donors.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Nov 28;14(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03575-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 38017497 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of extrachromosomal circular DNA in Wei and Large White pigs by high-throughput sequencing.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Feb 3;10:1085474. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1085474. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36816190 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

