A sePARate phase? Poly(ADP-ribose) versus RNA in the organization of biomolecular condensates
- PMID: 36243979
- PMCID: PMC9638928
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac866
A sePARate phase? Poly(ADP-ribose) versus RNA in the organization of biomolecular condensates
Abstract
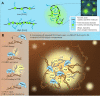
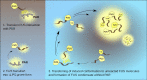
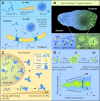
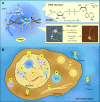
Condensates are biomolecular assemblies that concentrate biomolecules without the help of membranes. They are morphologically highly versatile and may emerge via distinct mechanisms. Nucleic acids-DNA, RNA and poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) play special roles in the process of condensate organization. These polymeric scaffolds provide multiple specific and nonspecific interactions during nucleation and 'development' of macromolecular assemblages. In this review, we focus on condensates formed with PAR. We discuss to what extent the literature supports the phase separation origin of these structures. Special attention is paid to similarities and differences between PAR and RNA in the process of dynamic restructuring of condensates during their functioning.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Biomolecular Condensates by Poly(ADP-ribose).Chem Rev. 2023 Jul 26;123(14):9065-9093. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00851. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Chem Rev. 2023. PMID: 37115110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose): A Dynamic Trigger for Biomolecular Condensate Formation.Trends Cell Biol. 2020 May;30(5):370-383. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.02.002. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Trends Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32302549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) in Condensates: The PARtnership of Phase Separation and Site-Specific Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 15;23(22):14075. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214075. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FUS Microphase Separation: Regulation by Nucleic Acid Polymers and DNA Repair Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 30;23(21):13200. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113200. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361989 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating biomolecular condensates: a novel approach to drug discovery.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022 Nov;21(11):841-862. doi: 10.1038/s41573-022-00505-4. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 35974095 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Divalent and multivalent cations control liquid-like assembly of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ated PARP1 into multimolecular associates in vitro.Commun Biol. 2024 Sep 15;7(1):1148. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06811-4. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39278937 Free PMC article.
-
Cation-induced intramolecular coil-to-globule transition in poly(ADP-ribose).Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 10;15(1):7901. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51972-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39256374 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of PARP1 and PAR in ATP-Independent Nucleosome Reorganisation during the DNA Damage Response.Genes (Basel). 2022 Dec 30;14(1):112. doi: 10.3390/genes14010112. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36672853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Biomolecular Condensates by Poly(ADP-ribose).Chem Rev. 2023 Jul 26;123(14):9065-9093. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00851. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Chem Rev. 2023. PMID: 37115110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G-Quadruplexes in Nuclear Biomolecular Condensates.Genes (Basel). 2023 May 13;14(5):1076. doi: 10.3390/genes14051076. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239436 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

