Cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles: emerging biomarkers and therapies for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma diagnosis/prognosis and treatment
- PMID: 36242076
- PMCID: PMC9563798
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-022-01641-0
Cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles: emerging biomarkers and therapies for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma diagnosis/prognosis and treatment
Abstract
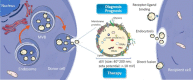
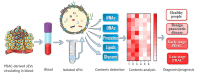
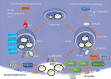
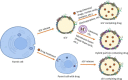
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the most fatal cancers worldwide with high mortality, which is mainly due to the lack of reliable biomarkers for PDAC diagnosis/prognosis in the early stages and effective therapeutic strategies for the treatment. Cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles (sEVs), which carry various messages and signal biomolecules (e.g. RNAs, DNAs, proteins, lipids, and glycans) to constitute the key features (e.g. genetic and phenotypic status) of cancer cells, are regarded as highly competitive non-invasive biomarkers for PDAC diagnosis/prognosis. Additionally, new insights on the biogenesis and molecular functions of cancer-derived sEVs pave the way for novel therapeutic strategies based on cancer-derived sEVs for PDAC treatment such as inhibition of the formation or secretion of cancer-derived sEVs, using cancer-derived sEVs as drug carriers and for immunotherapy. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the most recent scientific and clinical research on the discovery and involvement of key molecules in cancer-derived sEVs for PDAC diagnosis/prognosis and strategies using cancer-derived sEVs for PDAC treatment. The current limitations and emerging trends toward clinical application of cancer-derived sEVs in PDAC diagnosis/prognosis and treatment have also been discussed.
Keywords: Cancer diagnosis/prognosis; Cancer treatment; Extracellular vesicles; Pancreatic cancer.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phenotypic profiling of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma plasma-derived small extracellular vesicles for cancer diagnosis and cancer stage prediction: a proof-of-concept study.Anal Methods. 2022 Jun 16;14(23):2255-2265. doi: 10.1039/d2ay00536k. Anal Methods. 2022. PMID: 35612592
-
Differential Effects of Pancreatic Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Driving a Suppressive Environment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 27;24(19):14652. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914652. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834100 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative Proteomics Analysis Identified Differentially Expressed Proteins in Pancreatic Cancer-Associated Stellate Cell Small Extracellular Vesicles.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2022 Dec;21(12):100438. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2022.100438. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 36332889 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic Cancer Small Extracellular Vesicles (Exosomes): A Tale of Short- and Long-Distance Communication.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 28;13(19):4844. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194844. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34638330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics analysis of circulating small extracellular vesicles: Focus on the contribution of EVs to tumor metabolism.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023 Oct;73:3-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2023.08.003. Epub 2023 Aug 19. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023. PMID: 37652834 Review.
Cited by
-
A Current Synopsis of the Emerging Role of Extracellular Vesicles and Micro-RNAs in Pancreatic Cancer: A Forward-Looking Plan for Diagnosis and Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 17;25(6):3406. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063406. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small RNA sequencing analysis of peptide-affinity isolated plasma extracellular vesicles distinguishes pancreatic cancer patients from non-affected individuals.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 7;13(1):9251. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36370-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37286718 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid biopsy techniques and lung cancer: diagnosis, monitoring and evaluation.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 1;43(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03026-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38561776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting Nanomedicine for Cancer Polychemotherapy: Recent Advances and Clinical Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 14;15(3):937. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030937. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic significance of collagen signatures in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma obtained from second-harmonic generation imaging.BMC Cancer. 2024 May 29;24(1):652. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12412-5. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38811917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neoptolemos JP, Kleeff J, Michl P, Costello E, Greenhalf W, Palmer DH. Therapeutic developments in pancreatic cancer: current and future perspectives. Nat reviews Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:333–48. - PubMed
-
- Buscail L, Commentary Pancreatic cancer: is the worst to come? Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46:1774–5. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. 2020. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2020; 70: 7–30. - PubMed
-
- Kleeff J, Korc M, Apte M, La Vecchia C, Johnson CD, Biankin AV, et al. Pancreatic cancer. Nat Reviews Disease Primers. 2016;2:16022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

