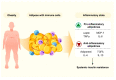
Beneficial Effects of Anti-Inflammatory Diet in Modulating Gut Microbiota and Controlling Obesity
- PMID: 36235638
- PMCID: PMC9572805
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14193985
Beneficial Effects of Anti-Inflammatory Diet in Modulating Gut Microbiota and Controlling Obesity
Abstract
Obesity has consistently been associated with an increased risk of metabolic abnormalities such as diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and cardiovascular diseases, as well as the development of several types of cancer. In recent decades, unfortunately, the rate of overweight/obesity has increased significantly among adults and children. A growing body of evidence shows that there is a relationship between metabolic disorders such as obesity and the composition of the gut microbiota. Additionally, inflammation is considered to be a driving force in the obesity-gut microbiota connection. Therefore, it seems that anti-inflammatory nutrients, foods, and/or diets can play an essential role in the management of obesity by affecting the intestinal flora and controlling inflammatory responses. In this review, we describe the links between the gut microbiota, obesity, and inflammation, and summarize the benefits of anti-inflammatory diets in preventing obesity.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory diets; dietary intervention; gut microbiota; inflammation; insulin resistance; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fat and not sugar as the determining factor for gut microbiota changes, obesity, and related metabolic disorders in mice.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Jan 1;324(1):E85-E96. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00141.2022. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 36516223
-
Gut microbiota determines the prevention effects of Luffa cylindrica (L.) Roem supplementation against obesity and associated metabolic disorders induced by high-fat diet.FASEB J. 2019 Sep;33(9):10339-10352. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900488R. Epub 2019 Jun 18. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31211921
-
Simultaneous Intake of Euglena gracilis and Vegetables Exerts Synergistic Anti-Obesity and Anti-Inflammatory Effects by Modulating the Gut Microbiota in Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Nutrients. 2019 Jan 21;11(1):204. doi: 10.3390/nu11010204. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30669573 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of the Triangular Relationship among Diet-Gut Microbiota-Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 29;25(17):9366. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179366. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between intestinal microbiota, adipose tissue and skeletal muscle as an early event in systemic low-grade inflammation and the development of obesity and diabetes.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015 Sep;31(6):545-61. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2617. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 25352002 Review.
Cited by
-
Management of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease/Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: From Medication Therapy to Nutritional Interventions.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 11;16(14):2220. doi: 10.3390/nu16142220. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39064665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in gut microbiota composition after 12 weeks of a home-based lifestyle intervention in breast cancer survivors during the COVID-19 lockdown.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 1;13:1225645. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1225645. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37727203 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Intake and Body Mass Index Influence the Risk of Islet Autoimmunity in Genetically At-Risk Children: A Mediation Analysis Using the TEDDY Cohort.Pediatr Diabetes. 2023;2023:3945064. doi: 10.1155/2023/3945064. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Pediatr Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37614409 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Foods: A Promising Strategy for Restoring Gut Microbiota Diversity Impacted by SARS-CoV-2 Variants.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 5;15(11):2631. doi: 10.3390/nu15112631. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37299594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of systemic immune-inflammation index with body mass index, waist circumference and prevalence of obesity in US adults.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 27;14(1):22086. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73659-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39333666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vetrani C., Di Nisio A., Paschou S.A., Barrea L., Muscogiuri G., Graziadio C., Savastano S., Colao A., on behalf of the Obesity Programs of Nutrition, Education, Research and Assessment (OPERA) Group From Gut Microbiota through Low-Grade Inflammation to Obesity: Key Players and Potential Targets. Nutrients. 2022;14:2103. doi: 10.3390/nu14102103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical