Neuroprotective Function of Rasagiline and Selegiline, Inhibitors of Type B Monoamine Oxidase, and Role of Monoamine Oxidases in Synucleinopathies
- PMID: 36232361
- PMCID: PMC9570229
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231911059
Neuroprotective Function of Rasagiline and Selegiline, Inhibitors of Type B Monoamine Oxidase, and Role of Monoamine Oxidases in Synucleinopathies
Abstract
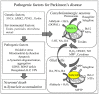
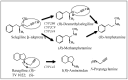
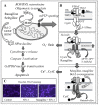
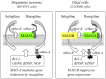
Synucleinopathies are a group of neurodegenerative disorders caused by the accumulation of toxic species of α-synuclein. The common clinical features are chronic progressive decline of motor, cognitive, behavioral, and autonomic functions. They include Parkinson's disease, dementia with Lewy body, and multiple system atrophy. Their etiology has not been clarified and multiple pathogenic factors include oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, impaired protein degradation systems, and neuroinflammation. Current available therapy cannot prevent progressive neurodegeneration and "disease-modifying or neuroprotective" therapy has been proposed. This paper presents the molecular mechanisms of neuroprotection by the inhibitors of type B monoamine oxidase, rasagiline and selegiline. They prevent mitochondrial apoptosis, induce anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein family, and pro-survival brain- and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factors. They also prevent toxic oligomerization and aggregation of α-synuclein. Monoamine oxidase is involved in neurodegeneration and neuroprotection, independently of the catalytic activity. Type A monoamine oxidases mediates rasagiline-activated signaling pathways to induce neuroprotective genes in neuronal cells. Multi-targeting propargylamine derivatives have been developed for therapy in various neurodegenerative diseases. Preclinical studies have presented neuroprotection of rasagiline and selegiline, but beneficial effects have been scarcely presented. Strategy to improve clinical trials is discussed to achieve disease-modification in synucleinopathies.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; gene induction; mitochondria; monoamine oxidase; multiple-targeted drugs; neuroprotection; rasagiline; selegiline; synucleinopathy; α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Type B and A monoamine oxidase and their inhibitors regulate the gene expression of Bcl-2 and neurotrophic factors in human glioblastoma U118MG cells: different signal pathways for neuroprotection by selegiline and rasagiline.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2017 Sep;124(9):1055-1066. doi: 10.1007/s00702-017-1740-9. Epub 2017 Jun 2. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2017. PMID: 28577058
-
Rasagiline and selegiline modulate mitochondrial homeostasis, intervene apoptosis system and mitigate α-synuclein cytotoxicity in disease-modifying therapy for Parkinson's disease.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2020 Feb;127(2):131-147. doi: 10.1007/s00702-020-02150-w. Epub 2020 Jan 28. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2020. PMID: 31993732 Review.
-
Rasagiline and selegiline, inhibitors of type B monoamine oxidase, induce type A monoamine oxidase in human SH-SY5Y cells.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2013 Mar;120(3):435-44. doi: 10.1007/s00702-012-0899-3. Epub 2012 Sep 12. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2013. PMID: 22968599
-
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors as neuroprotective agents in age-dependent neurodegenerative disorders.Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(25):2799-817. doi: 10.2174/138161210793176527. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 20698822 Review.
-
Toxic interactions between dopamine, α-synuclein, monoamine oxidase, and genes in mitochondria of Parkinson's disease.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2024 Jun;131(6):639-661. doi: 10.1007/s00702-023-02730-6. Epub 2024 Jan 9. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2024. PMID: 38196001 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploitation of the multitarget role of new ferulic and gallic acid derivatives in oxidative stress-related Alzheimer's disease therapies: design, synthesis and bioevaluation.RSC Adv. 2024 Mar 28;14(15):10304-10321. doi: 10.1039/d4ra00766b. eCollection 2024 Mar 26. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38549798 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of monoamine oxidases by heterocyclic derived conjugated dienones: synthesis and in vitro and in silico investigations.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Sep 12;16(1):221-31. doi: 10.1039/d4md00608a. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39430951
-
Xanthine-Dopamine Hybrid Molecules as Multitarget Drugs with Potential for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Biomolecules. 2023 Jul 5;13(7):1079. doi: 10.3390/biom13071079. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37509114 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Synthesis of Multi-Functional Ligands through Hantzsch Reaction: Targeting Ca2+ Channels, Activating Nrf2 and Possessing Cathepsin S Inhibitory, and Antioxidant Properties.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jan 17;16(1):121. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010121. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38258131 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating Stress Proteins in Response to Therapeutic Interventions for Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 12;24(22):16233. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216233. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003423 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Knoll J., Magyar K. Some puzzling pharmacological effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmacol. 1972;5:393–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

