Macrophages, Chronic Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance
- PMID: 36230963
- PMCID: PMC9562180
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11193001
Macrophages, Chronic Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance
Abstract
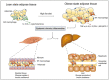
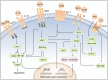
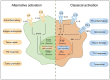
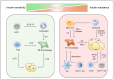
The prevalence of obesity has reached alarming levels, which is considered a major risk factor for several metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes (T2D), non-alcoholic fatty liver, atherosclerosis, and ischemic cardiovascular disease. Obesity-induced chronic, low-grade inflammation may lead to insulin resistance, and it is well-recognized that macrophages play a major role in such inflammation. In the current review, the molecular mechanisms underlying macrophages, low-grade tissue inflammation, insulin resistance, and T2D are described. Also, the role of macrophages in obesity-induced insulin resistance is presented, and therapeutic drugs and recent advances targeting macrophages for the treatment of T2D are introduced.
Keywords: chronic inflammation; insulin resistance; macrophages; molecular mechanism; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolic and Molecular Mechanisms of Macrophage Polarisation and Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 10;21(16):5731. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165731. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32785109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of SGLT2 inhibitors in obesity and insulin resistance: Focus on fat browning and macrophage polarization.Adipocyte. 2018;7(2):121-128. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2017.1413516. Epub 2018 Jan 29. Adipocyte. 2018. PMID: 29376471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meta-Inflammation and Metabolic Reprogramming of Macrophages in Diabetes and Obesity: The Importance of Metabolites.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 5;12:746151. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.746151. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34804028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose tissue macrophages in the development of obesity-induced inflammation, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.Arch Pharm Res. 2013 Feb;36(2):208-22. doi: 10.1007/s12272-013-0023-8. Epub 2013 Feb 10. Arch Pharm Res. 2013. PMID: 23397293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A narrative review: CXC chemokines influence immune surveillance in obesity and obesity-related diseases: Type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2023 Aug;24(4):611-631. doi: 10.1007/s11154-023-09800-w. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2023. PMID: 37000372 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association Apo B/Apo a-1 Ratio and Prognostic Nutritional Index with 90-Day Outcomes of Acute Ischemic Stroke.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Aug 13;17:3009-3018. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S473385. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39155912 Free PMC article.
-
The Interplay between Obesity and Inflammation.Life (Basel). 2024 Jul 8;14(7):856. doi: 10.3390/life14070856. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39063610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of intestinal microenvironments in obesity and bariatric surgery on shaping macrophages.Immunometabolism (Cobham). 2023 Nov 28;5(4):e00033. doi: 10.1097/IN9.0000000000000033. eCollection 2023 Oct. Immunometabolism (Cobham). 2023. PMID: 38037591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ziziphus jujuba (Jujube) in Metabolic Syndrome: From Traditional Medicine to Scientific Validation.Curr Nutr Rep. 2024 Dec;13(4):845-866. doi: 10.1007/s13668-024-00581-5. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Curr Nutr Rep. 2024. PMID: 39354208 Review.
-
Epigenetic and Molecular Alterations in Obesity: Linking CRP and DNA Methylation to Systemic Inflammation.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 13;46(7):7430-7446. doi: 10.3390/cimb46070441. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39057082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zubrzycki A., Cierpka-Kmiec K., Kmiec Z., Wronska A. The role of low-calorie diets and intermittent fasting in the treatment of obesity and type-2 diabetes. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018;69:663–683. - PubMed
-
- Singh G.M., Danaei G., Farzadfar F., Stevens G.A., Woodward M., Wormser D., Kaptoge S., Whitlock G., Qiao Q., Lewington S., et al. The age-specific quantitative effects of metabolic risk factors on cardiovascular diseases and diabetes: A pooled analysis. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e65174. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065174. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

