POP1 inhibits MSU-induced inflammasome activation and ameliorates gout
- PMID: 36225929
- PMCID: PMC9550078
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.912069
POP1 inhibits MSU-induced inflammasome activation and ameliorates gout
Abstract
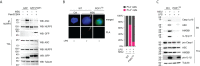
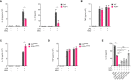
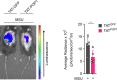
Canonical inflammasomes are innate immune protein scaffolds that enable the activation of inflammatory caspase-1, and subsequently the processing and release of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-18, and danger signals, as well as the induction of pyroptotic cell death. Inflammasome assembly and activation occurs in response to sensing of infectious, sterile and self-derived molecular patterns by cytosolic pattern recognition receptors, including the Nod-like receptor NLRP3. While these responses are essential for host defense, excessive and uncontrolled NLRP3 inflammasome responses cause and contribute to a wide spectrum of inflammatory diseases, including gout. A key step in NLRP3 inflammasome assembly is the sequentially nucleated polymerization of Pyrin domain (PYD)- and caspase recruitment domain (CARD)-containing inflammasome components. NLRP3 triggers polymerization of the adaptor protein ASC through PYD-PYD interactions, but ASC polymerization then proceeds in a self-perpetuating manner and represents a point of no return, which culminates in the activation of caspase-1 by induced proximity. In humans, small PYD-only proteins (POPs) lacking an effector domain regulate this key process through competitive binding, but limited information exists on their physiological role during health and disease. Here we demonstrate that POP1 expression in macrophages is sufficient to dampen MSU crystal-mediated inflammatory responses in animal models of gout. Whether MSU crystals are administered into a subcutaneous airpouch or into the ankle joint, the presence of POP1 significantly reduces neutrophil infiltration. Also, airpouch exudates have much reduced IL-1β and ASC, which are typical pro-inflammatory indicators that can also be detected in synovial fluids of gout patients. Exogenous expression of POP1 in mouse and human macrophages also blocks MSU crystal-induced NLRP3 inflammasome assembly, resulting in reduced IL-1β and IL-18 secretion. Conversely, reduced POP1 expression in human macrophages enhances IL-1β secretion. We further determined that the mechanism for the POP1-mediated inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation is through its interference with the crucial NLRP3 and ASC interaction within the inflammasome complex. Strikingly, administration of an engineered cell permeable version of POP1 was able to ameliorate MSU crystal-mediated inflammation in vivo, as measured by neutrophil infiltration. Overall, we demonstrate that POP1 may play a crucial role in regulating inflammatory responses in gout.
Keywords: caspase-1; gout; inflammasome; inflammation; macrophage; pyrin domain.
Copyright © 2022 de Almeida, Devi, Indramohan, Huang, Ratsimandresy, Pope, Dorfleutner and Stehlik.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

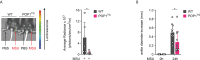
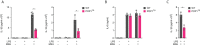
Similar articles
-
POP1 might be recruiting its type-Ia interface for NLRP3-mediated PYD-PYD interaction: Insights from MD simulation.J Mol Recognit. 2017 Sep;30(9). doi: 10.1002/jmr.2632. Epub 2017 Apr 3. J Mol Recognit. 2017. PMID: 28370480
-
NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neutrophil recruitment and hypernociception depend on leukotriene B(4) in a murine model of gout.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Feb;64(2):474-84. doi: 10.1002/art.33355. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 21952942
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the Innate Immune Response to Gout.Immunol Invest. 2023 Apr;52(3):364-397. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2023.2168554. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Immunol Invest. 2023. PMID: 36745138 Review.
-
The PYRIN Domain-only Protein POP1 Inhibits Inflammasome Assembly and Ameliorates Inflammatory Disease.Immunity. 2015 Aug 18;43(2):264-76. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.07.018. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Immunity. 2015. PMID: 26275995 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on CARD Only Proteins (COPs) and PYD Only Proteins (POPs) as Inflammasome Regulators.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 20;21(18):6901. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186901. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32962268 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Foundations of Inflammatory Diseases: Insights into Inflammation and Inflammasomes.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jan 3;46(1):469-484. doi: 10.3390/cimb46010030. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38248332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design principles for inflammasome inhibition by pyrin-only-proteins.Elife. 2024 Jan 22;13:e81918. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81918. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38252125 Free PMC article.
-
TCM and related active compounds in the treatment of gout: the regulation of signaling pathway and urate transporter.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 29;14:1275974. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1275974. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38094893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of SOCS3 and PTGS2 as new biomarkers for the diagnosis of gout by cross-species comprehensive analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 23;10(9):e30020. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30020. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38707281 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoupled pyroptosis and IL-1β secretion downstream of inflammasome signaling.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 6;14:1128358. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1128358. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37090724 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

